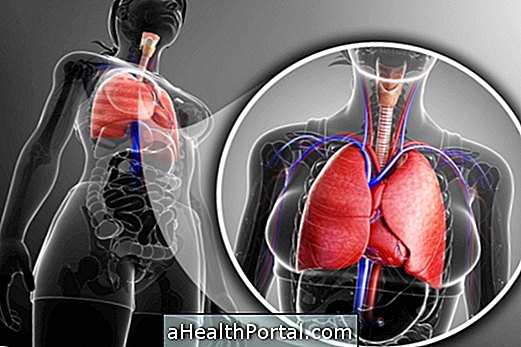
Treatment for lung cancer can be done with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy or photodynamic therapy, depending on the type of cancer, size, location of the tumor, and overall health status of the patient.
Lung cancer has a greater chance of cure when it is diagnosed early and treatment is followed correctly.
1. Surgery for lung cancer
The surgery for lung cancer is done aiming to remove the tumor and lymph nodes near the affected lung to prevent the progression of the disease and metastasis, which is the spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body. Thus, surgery can be of three types:
- Segmentectomy, in which a small part of the lung lobe is removed with cancer. It is indicated for patients with small tumors or those who are in poor health;
- Lobectomy, in which an entire lobe of the lung is removed. This type of surgery is best suited for lung cancer, even when the tumors are small;
- Pneumectomy, which corresponds to removal of the entire lung from the side affected by cancer. It is indicated when the tumor is located near the center of the thorax.
Recovery time for surgery is time-consuming and complications such as difficulty breathing, bleeding, infections, or pneumonia can occur with the use of medications or respiratory therapy. Physiotherapeutic treatment for lung cancer is very important because it helps to improve and increase the capacity of expansion of the chest during breathing, being indicated before and after the surgery.
2. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for lung cancer aims to destroy cancer cells, located in the lung or scattered throughout the body, and is usually performed by administering medications directly into the vein, by injection or catheter. Chemotherapy treatment can last for 1 year or more and is done according to the type, extent, and severity of the cancer.
Chemotherapy can be performed before surgery to reduce the tumor and make it easier to withdraw or can be performed after surgery to destroy cancer cells that may still remain in the body. In cases where surgery is contraindicated and in cases of advanced cancers, chemotherapy is the main treatment used to control tumor growth and relieve symptoms of the disease.
Generally, chemotherapy uses the combination of 2 medications such as Cisplatin, Etoposide, Gefitinib, Paclitaxel, Vinorelbine or Vimblastine. However, side effects related to the use of these medications, such as hair loss, inflammation of the mouth, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea or constipation, infections, blood disorders and extreme tiredness, for example, are common. Understand how chemotherapy is done.
Most side effects disappear after treatment is finished, but in some cases analgesics or sickness medicines may be used to relieve symptoms and make treatment easier to follow.

3. Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is indicated when the person can not be operated due to the location or size of the tumor. In this type of treatment, the radiation is used to destroy the cancer cells, and external radiation can be applied through a machine that emits radiation beams, or by brachytherapy, in which the radioactive material is placed next to the tumor.
Radiation therapy, as well as chemotherapy, can also be performed before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor, or else to destroy the cancer cells that may still be in the lung. However, this type of treatment can also result in side effects such as fatigue, loss of appetite, sore throat, inflammation where radiation is applied, fever, cough and shortness of breath, for example.
Side effects usually go away at the end of treatment, but some symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath and fever, indicative of inflammation of the lungs, may persist for a few months. Learn how to relieve the side effects of radiation therapy.
4. Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy for lung cancer is used in the early stages of disease when it is necessary to open the airways obstructed by tumors in the lungs. This therapy consists of the use of a special medicine, which is injected into the bloodstream in order to accumulate in the cancerous cells.
After accumulation of the drug in the tumor, a laser is applied at the site to kill the cancer cells that are then removed through a bronchoscopy. Photodynamic therapy can cause airway swelling for a few days, causing shortness of breath, coughing up blood and phlegm, which can be treated at the hospital.