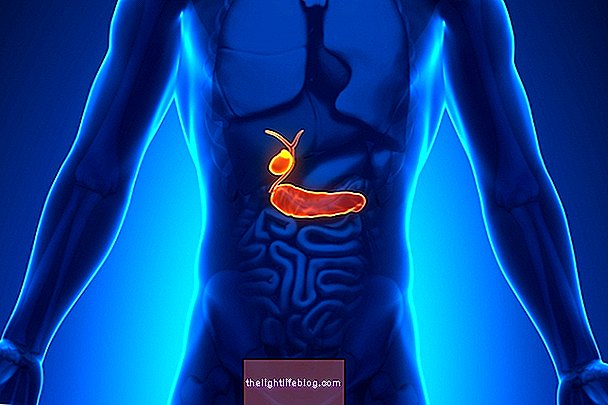
Liver cancer is a type of malignant tumor that originates in cells that form the liver, such as hepatocytes, bile ducts or blood vessels, and is generally quite aggressive. It can cause symptoms, which usually arise in the more advanced stages of the disease, and include pain in the abdomen, motion sickness, loss of appetite, weight loss and yellowing eyes.
People with liver fat, liver cirrhosis or using anabolic steroids are at increased risk for developing this cancer, which is usually identified by imaging the abdomen, such as ultrasound or tomography, that can detect one or more nodules in the liver.
The treatment is done with surgery and chemotherapy, depending on the size and severity of each case, and the chances of cure are greater when the tumor is identified early, in the earliest stages. When liver cancer can no longer be cured, the survival time is approximately 5 years, but this value may vary according to the degree of disease development and other diseases of the patient.

Symptoms that may indicate cancer
The most common symptoms that can arise in liver cancer include:
- Pain in the belly, especially on the right side of the abdomen;
- Swelling of the belly;
- Loss of weight without apparent cause;
- Loss of appetite;
- Excessive tiredness;
- Skin and yellow eyes;
- Constant discomfort.
Unfortunately these symptoms usually arise when the cancer is already well developed and therefore, in most cases, liver cancer can be discovered at an advanced stage, which decreases your chances of cure.
Thus, when there are risk factors, such as excessive alcohol consumption or liver disease, it is important to have regular consultations with the hepatologist to assess the liver frequently and see any changes that may occur.
What to do in case of suspicion
In cases where any of these symptoms arise or there are many risk factors, it is advisable to consult a hepatologist for diagnostic tests such as ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging to confirm if there are any changes that may indicate the presence of a spot or nodule that is suggestive of tumor.
It is important to remember that not every nodule or cyst in the liver indicates cancer, and should wait for the doctor's analysis of his characteristics, and can determine if there is risk or not. If suspicious changes are identified, the doctor may order a biopsy of a piece of liver to check in the laboratory whether there are any cancer cells in the organ. Understand when the cyst in the liver is dangerous.
For the less suspect cases, it is recommended to repeat the tests periodically, every year or every 3 years, according to each case, so that it is possible to monitor if there is growth or development of new characteristics that may indicate cancer.

Who is most at risk
Although anyone can develop liver cancer, this type of cancer is more common in people with:
- Chronic infection with Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C;
- Cirrhosis;
- Use of anabolic steroids;
- Diabetes;
- Fat in the liver;
- Excessive consumption of alcohol.
In addition, cases of ulcerative colitis or long-lasting sclerosing cholangitis may also develop liver cancer more easily.
How is the treatment done?
In almost all cases, liver cancer treatment is done with surgery to remove the entire affected area. However, chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be necessary before surgery to decrease the size of the cancer and facilitate its removal.
In more severe cases, where the cancer is highly developed or spreading to other organs, chemotherapy and radiotherapy can also be used only after surgery to try to eliminate the remaining cancerous cells.
If there is another disease, such as cirrhosis, removal of a part of the liver can be more complicated, so your doctor may recommend a liver transplant to try to reach a cure. Learn more about this form of treatment.
What are the types
Liver cancer can be primary, ie when it appears directly in the liver, or it may be secondary, by metastasis or spread of cancer from other organs such as lungs, stomach, intestine or breast, for example.
The most common type of primary cancer of the liver is hepatocellular carcinoma or hepatocellular carcinoma, which is also the most aggressive, and originates in the major cells that form the liver, called hepatocytes. Another common primary tumor is cholangiocarcinoma, which originates in the bile ducts. Learn more about the symptoms and treatment of bile duct cancer.
Other more rare tumor types include fibrolamellar variant hepatic carcinoma, angiosarcoma or hepatoblastoma, for example.