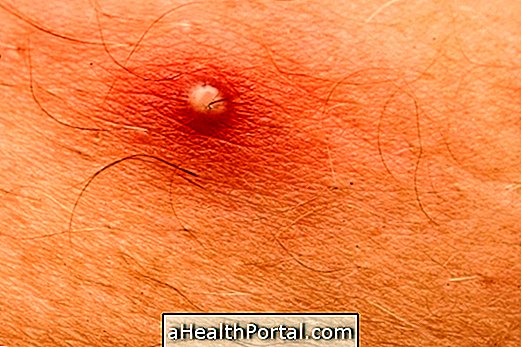
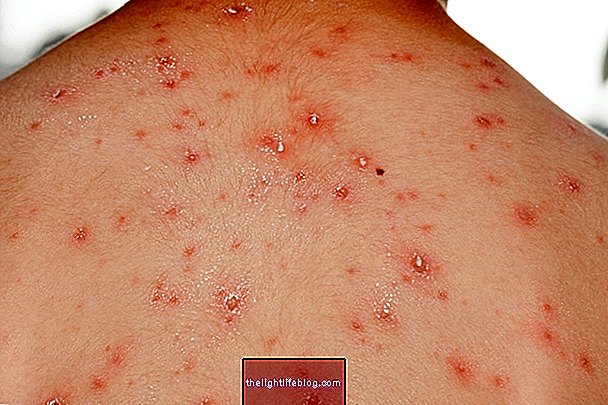
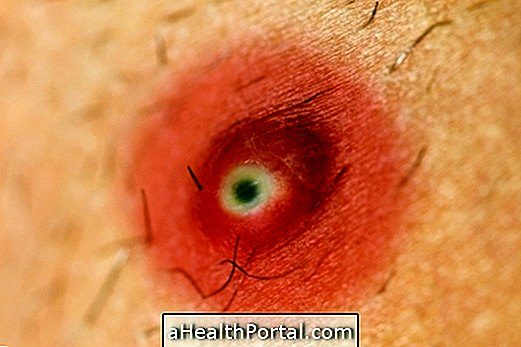
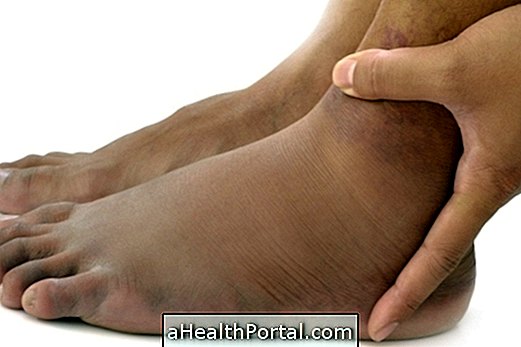
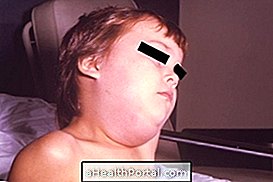
Hidradenitis suppurativa, also known as reverse acne, is a rare skin disease that causes painful lumps to appear underneath the skin, which can rupture and cause foul smells, leaving a scar on the skin when they disappear.
Although this problem may arise in any region of the body, it is more common in places where the skin is rubbing, such as in the armpits, groin, buttocks or under the breasts, for example.
Although hidradenite has no cure, it can be controlled with medicines and ointments to prevent the appearance of new lumps and the appearance of more complications.

Main symptoms
Symptoms can occur at any age, however they are more common after age 20 and include:
- Inflammation of the skin with lumps of various sizes or blackheads;
- Severe redness at the affected site;
- Intense and constant pain;
- Excessive sweating in the region;
- Formation of channels under the cores.
In some cases, the lumps can rupture and release pus, causing odor to appear on the site, in addition to causing more pain.
The lumps can take several weeks and even months to disappear, being bigger and more painful in people with excess weight, constant stress or who are in a period of great hormonal changes, like puberty or pregnancy.
How to confirm the diagnosis
After the onset of these symptoms, without improvement in 2 weeks, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis only by observing the affected site, in order to initiate the appropriate treatment and relieve the symptoms.
When done quickly, the diagnosis can help lessen the chances of worsening of the condition, as well as the appearance of complications such as deep scars that can hinder the movement of the affected limb and cause frequent contractures, for example.
How to treat
Treatment for suppurative hidradenitis, although it does not cure the disease, helps to alleviate the symptoms and prevent their onset so often, also decreasing the chances of having complications.
Some of the most commonly used ways to treat idradenitis include:
- Antibiotic tablets or ointments, such as Tetracycline, Clindomycin or Erythromycin: eliminate bacteria from the skin, avoiding an infection of the site that can aggravate the complications;
- Vitamin A ointments, such as Hypoglossus or Hypodermis: help the skin to heal faster;
- Injections of corticosteroids, such as Prednisolone or Triamcinolone: reduce inflammation of the lump, relieving swelling, pain and redness;
- Analgesics such as Paracetamol or Ibuprofen help relieve discomfort and pain.
In addition, the dermatologist may also prescribe some remedies that help decrease the action of the immune system, such as Infliximab or Adalimumab, because they avoid the effect of a protein that seems to worsen cases of hidradenite.
In the more severe cases, where the symptoms are more intense and there is exaggerated swelling, infection or formation of canals, the doctor may also advise surgery to remove the affected limbs and the affected skin. In these cases, you need to have a skin transplant, which is usually removed from other parts of the body.