Mycosis of the skin is a type of disease caused by the presence of fungi on the skin, which causes itching, redness and peeling and can reach any region of the body, being more frequent in summer, since heat and sweat favor the multiplication of fungi they inhabit the skin, causing the infection. See more symptoms of ringworm.
There are several types of skin mycoses that can be classified depending on the affected area and the fungus that is at its source.
1. Nail fungus
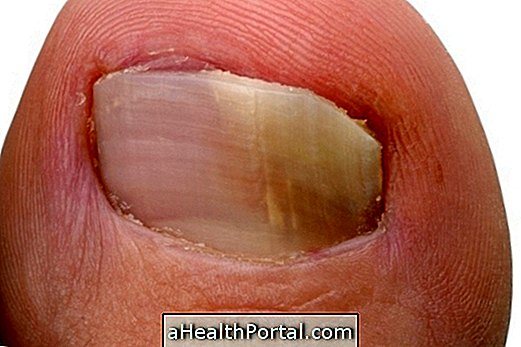
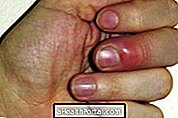
Also known as onychomycosis, it is an infection that leaves the nails yellowish, deformed and thick, and can be transmitted to areas around the nail or other nails, being more frequent in the nails of the foot.
How to treat: Nail mycosis can be treated with tablets, prescribed by the dermatologist, such as Fluconazole or Itraconazole, or by passing an ointment or enamel for nail fungus such as Loceryl, Micolamina or Fungirox, for example . Another option is the use of laser, which removes the fungus from mycosis through the infrared rays emitted by it.
The treatment for nail fungus is time consuming because the fungus is only completely eliminated when the nail grows. Therefore, the treatment usually takes about 6 months for mycosis of the fingernails and 12 months for mycosis of the toenails. Learn more about nail fungus.
2. Candidiasis

Candidiasis is an infection caused by the fungus Candida albicans that manifests in the mouth, on the female or male genitals.
Vaginal candidiasis is a very common infection in women due to the increased population of this fungus , which is normally present in the flora of the woman's intimate region, but develops when the immune system is weakened, in cases of diabetes, when there are bad habits hygiene or after treatment with some antibiotics or corticosteroids.
Oral candidiasis is an infection that mainly affects babies due to their immunity still undeveloped, or in adults with immune system weakened due to flu, chronic diseases or HIV, for example.
How to treat: Treatment for oral candidiasis can be done at home with antifungal agents in the form of a gel, liquid or mouthwash, such as Nystatin, for 5 to 7 days, however, in more severe cases, treatment may be taken with oral antifungal medicines, such as Fluconazole, as directed by your doctor. See the treatment for oral candidiasis in more detail.
In the case of candidiasis on the genitals, it is possible to use oral or local ointments and tablets, such as fluconazole, clotrimazole or ketoconazole. Learn more about how to treat candidiasis.
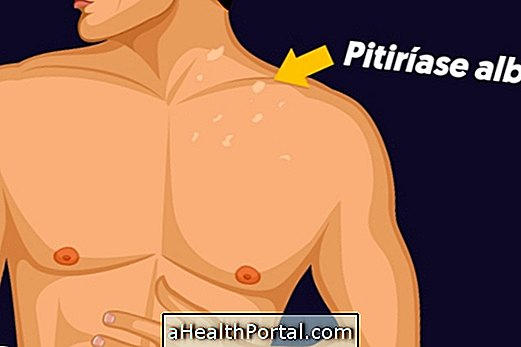
3. Pityriasis versicolor

Also known as white cloth or beach mycosis, it is a type of mycosis caused by the fungus Malassezia furfur, which produces a substance that prevents the skin from producing melanin when exposed to the sun. Thus, in the places where the fungus is, the skin does not get tanned, leading to the appearance of small white spots. Learn more about this type of ringworm.
How to treat: The treatment for beach mycosis is done with the use of medicines such as Fluconazole, or antifungal applied on the spot, such as creams, ointments, lotions or sprays, depending on the degree of skin involvement. If the ringworm comes back soon after the treatment, it is necessary to go to the dermatologist for a specific treatment.
4. Athlete's Foot

Also known as had pedis or frieira, this is a type of ringworm of the skin caused by fungi Trichophyton, Microsporum or Epidermophyton, which mainly affects regions in the sole and between the toes.
How to treat: Treatment usually consists of the application of antifungal creams or ointments, but in some cases the symptoms may not only improve with the use of this type of creams and, therefore, it may be necessary for the doctor to prescribe Itraconazole antifungal tablets, Fluconazole or Terbinafine for about 3 months. Learn more about this ringworm and how to treat it.
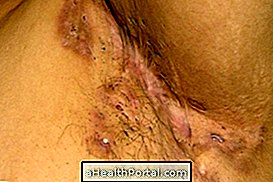
5. Ringworm in the groin

Also called cruralis, this mycosis is caused by the fungus Tinea cruris, being more frequent in obese, athletes or people who wear clothes too tight, due to the creation of a warm and humid environment, favorable to its development.
How to treat: Treatment usually consists of the application of antifungal creams or ointments such as clotrimazole or econazole.
6. Had scalp

Also known as Tinea capitis, this is a ringworm that can be caused by different fungi, which can lead to hair loss, scalp psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, among others.
How to treat: Treatment consists of the use of shampoos or lotions with tar or salicylic acid or with clobetasol propionate, and may be associated with an antifungal, such as ketoconazole. See more about treating psoriasis on the scalp.
7. Impingem

This ringworm, also known as had corporis, can develop in any region of the body, and is characterized by a red rash with lighter skin in the middle. Learn how to identify and treat Impingem.
How to treat: In most cases, the treatment is done with the application of antifungal creams and ointments such as clotrimazole, ketoconazole, isoconazole or terbinafine; however, if the symptoms do not improve with the use of this type of cream, one should go your doctor to prescribe antifungal tablets like fluconazole or terbinafine for example.
During treatment of a ringworm, some home remedies may still be used to relieve symptoms more quickly.
Home Treatments for Skin Ringworm
Ringworm can also be treated or alleviated with the use of home remedies such as passing a clove of garlic with chlorhexidine on your nails or dipping your feet in a bowl of peppermint tea.
A great home remedy for candidiasis in women is to introduce the natural yogurt into the vagina. Yogurt will decrease the acidity of the vagina, halting the growth of fungi that prefer a more acidic environment to develop. This home remedy can also be used by men. See more home remedies for treating candidiasis.
Possible causes
Fungi are the main cause of mycoses in the skin, however, for the disease to develop, it is necessary to meet other conditions, such as depression of the immune system, a hot and humid environment and, moreover, in most cases contagion is necessary.
The infection may appear more frequently after taking antibiotics, because the bacteria present on the skin decrease, allowing fungi to proliferate. In addition, walking barefoot in public places such as beaches, swimming pools and restrooms, having poor blood circulation, nail injuries, having unprotected sex, taking excessive showers, sweating a lot, wearing tight clothing and frequenting places that are too humid and hot increases the risk of developing ringworm.









.jpg)