Symptoms of typhoid and paratyphoid, similar infectious diseases caused by the bacterium Salmonella, but of different strains , include:
- High fever;
- Reddish spots on the skin, especially on the chest and abdomen;
- Tummy and headache;
- Gastrointestinal problems, such as vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation;
- Liver and spleen enlargement;
- Loss of appetite and weight;
- Swelling of the belly;
- Cough;
- Depression.
The incubation period of the disease is about 1 to 3 weeks, so initially the symptoms are mild, but they get worse in the first three weeks after the infection, starting to regress in the fourth week with the treatment.
Typhoid fever is usually transmitted when the individual drinks water or ingests food contaminated with feces or urine from an individual who is sick or has no symptoms of the disease but still contains the bacteria that causes typhoid.
Other forms of contagion are through anal sex or when the healthy individual, after having direct contact with the dirty hand of the sick individual or who still contains the bacterium, takes his hand to his mouth.
Treatment for typhoid fever
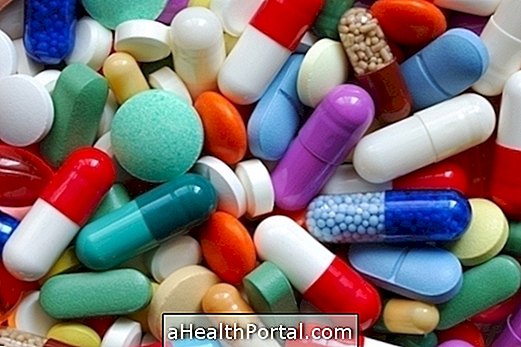
The treatment for typhoid fever can be done with antibiotics, resting and fluid intake for the patient to stay hydrated and, in severe cases, hospital admission may be necessary.
Prevention of typhoid fever
The prevention of typhoid fever can be done with the typhoid vaccine, daily hygiene care, frequent garbage collection, correct preparation of food, boiling or filtration of water before being drunk and cleaning every 6 months of the box d ' Water.
Useful links:
- Treatment for typhoid fever
- Typhoid fever
- Cholera