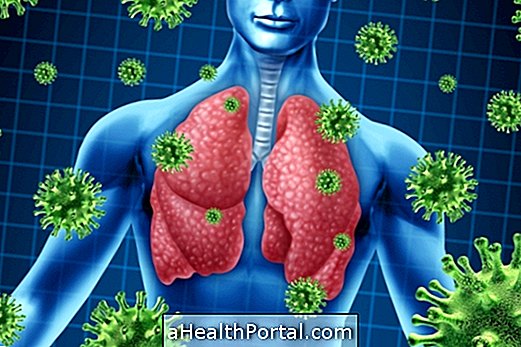
Pulmonary infection, also called respiratory infection, can be acute, when it appears in 7 days, or chronic, when it gradually arises. It can be caused by viruses, parasites, fungi or bacteria, which enter the airways and lodge in the lungs, generating symptoms such as fever, cough, catarrh and difficulty breathing. Your treatment is done with antibiotics in hospital or at home, depending on the state of health of the individual.
When it is identified early and its treatment starts quickly, it has about a 80% chance of cure within 15 days, even in the elderly. However, patients with a low immune system, such as in the case of AIDS and in patients undergoing cancer treatment, may be longer than usual.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Infection
The symptoms of lung infection are:
- Fever
- Difficulty breathing
- Catarrh
- Cough
Ear pain and sore throat may also be present before the lung picture in some individuals. Learn more at: Symptoms of lung infection.
How to identify lung infection
To identify pulmonary infection, the physical examination of the individual is recommended, in which color, temperature, secretions, pulmonary auscultation, state of consciousness, and complementary exams such as blood and chest X-ray are observed.
When the diagnosis is made, treatment is started, but it is important to identify the causative agent of the infection to adopt the best course of treatment, and this can be achieved with laboratory analysis of the sputum.
Treatment of lung infection
The treatment for pulmonary infection is done with medicines that act directly against the causative agent, the antibiotics, antifungals or antiparasitarios, for example. You can also use medicines for pain and to lower the fever.
To complement the treatment, one can indicate respiratory physiotherapy, performed with respiratory exercises and small devices that help to eliminate the secretions of the lungs, bringing relief of the symptoms. In addition, healthy eating and good hydration are also important in the recovery period and during the treatment of lung infection.
Pulmonary infections can also be caused by work where there is a daily inhalation of particles and dust, as in the case of bricklayers, carpenters, general cleaning services. See other diseases caused by the performance of professional activity in 5 Diseases that may arise at work and how to treat.