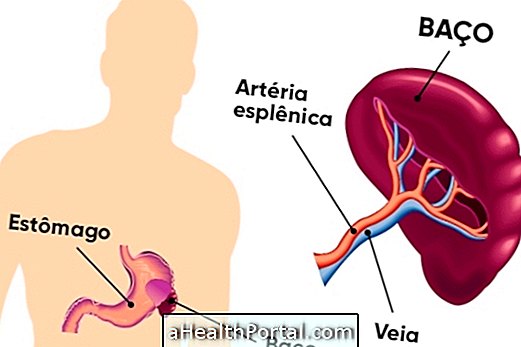
Isotopic cisternography is a nuclear medicine exam that takes a kind of radiography with contrast of the brain and spine that allows to evaluate and diagnose changes in the flow of the cerebrospinal fluid, caused by fistulas that allow the passage of this liquid to other places of the body.
This test is performed after an injection of a substance that is a radiopharmaceutical, such as Tc99m or In11, through a lumbar puncture, which allows the substance to pass through the spine until it reaches the brain. In the case of a fistula, magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography will show the presence of this substance in other structures of the body as well.
What is Cisternografia used for?
Cerebral cisternography is used to determine the diagnosis of cerebrospinal fluid leakage, which is a small 'hole' in the tissue that lines the central nervous system composed of the brain and spinal cord, allowing the passage of cerebrospinal fluid to other parts of the body.
The great disadvantage of this examination is that it requires several brain images made in several sessions, and may need to be done in a few days in a row for a correct diagnosis. In some cases when the patient is very agitated it is necessary to administer tranquilizers before the examination.
How is this exam done?
Cystronography is an examination that requires many sessions of brain imaging, which must be taken for two to three days in a row. Therefore, it may be necessary to hospitalize the patient and often to sedation.
To perform the cerebral cisternography examination it is necessary to:
- Apply anesthetic at the injection site and draw a sample of the liquid from the column that will be mixed with the contrast;
- A contrast injection should be given at the end of the patient's spine and the nostrils should be capped with cotton;
- The patient should lie down for a few hours with his feet slightly higher than the rest of the body;
- X-ray images of the thorax and head are then performed after 30 minutes, and then repeated after 4, 6, 12, and 18 hours of application of the substance. Sometimes it may be necessary to repeat the examination after a few days.
A rest period of 24 hours is required after the test, and the result will show the presence of a CSF fistula, or not.
Contraindications
Cerebral cisternography is contraindicated in cases of increased intracranial pressure in pregnant women because of the risk of radiation to the fetus.
Where to do
Isotopic cisternography can be performed at clinics or a nuclear medicine hospital.