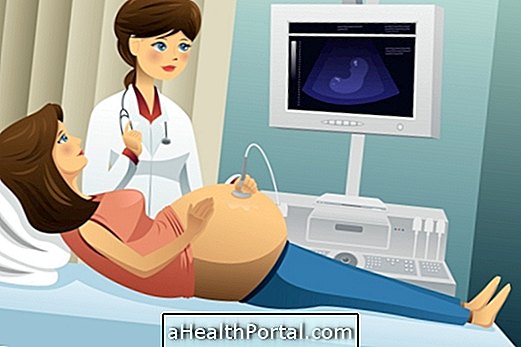
The diagnosis of Down Syndrome can be made during pregnancy through specific tests such as nuchal translucency, cordocentesis and amniocentesis, which not every pregnant woman needs to do. These tests are always requested by the obstetrician when the mother becomes pregnant more than 35 years of age or when the pregnant woman has Down Syndrome.
These tests can also be ordered when the woman has had a baby with Down Syndrome if the obstetrician observes any changes in the ultrasound that causes her to suspect the syndrome or if the baby's father has the chromosomal translocation involving the chromosome 21.
The pregnancy of a baby with Down syndrome is exactly the same as a baby who does not have this syndrome, however, more tests are needed to assess the baby's developmental health, which should be a little smaller and have less weight for the baby. gestational age.
Exams for diagnosis during pregnancy
The tests that give 99% accuracy in the outcome and serve to prepare parents for the reception of a baby Down Syndrome are:
| When it is done | Exam | How is done |
| 9 weeks gestation | Collection of chorionic villi | It consists of the withdrawal of a small quantity of placenta, that possesses genetic material identical to the one of the baby |
| 10th to 14th week of gestation | Maternal Biochemist | It involves performing two tests that measure the amount of a protein and the amount of hormone Beta HCG produced in pregnancy by the placenta and the baby |
| 12 weeks gestation | Nuchal translucency | It can be performed with an ultrasound that measures the length of the baby's neck |
| 13th to 16th week of gestation | Amniocentesis | It consists of withdrawing a sample of the amniotic fluid |
| 18 weeks gestation | Cordocentesis | Consists of withdrawing a sample of blood from the baby by the umbilical cord |
When knowing the diagnosis, parents should ideally look for information about the syndrome to know what to expect in the growth of a child with Down Syndrome. Learn more details of the characteristics and treatment needed in: How is life after Down Syndrome Diagnosis.
How is the diagnosis after birth

The diagnosis after birth can be made after observing the characteristics that the baby has, which may include:
- Another line in the eyelid of the eyes, that leave them more closed and pulladinhos to the side and up;
- Only 1 line in the palm of the hand, although other children who do not have Down Syndrome may also have these characteristics;
- Union of eyebrows;
- Narrower nose;
- Flat face;
- Big tongue, sky high in the mouth;
- Lower and smaller ears;
- Thin, thin hair;
- Short fingers, and pinky can be crooked;
- Greater distance between the big toes of other fingers;
- Wide neck and fat accumulation;
- Weakness of the muscles of the whole body;
- Ease to gain weight;
- You may have umbilical hernia;
- Increased risk of celiac disease;
- There may be a withdrawal of the rectus abdominis muscles, which makes the abdomen more flaccid.
The more characteristics the baby presents the greater the chances of having Down's Syndrome, however about 5% of the population also presents some of these characteristics and having only one of them is not indicative of this syndrome.
Other features of the syndrome include the presence of heart disease, which may require surgery and a higher risk of ear infections, but each person has his or her own alterations and therefore each baby with this syndrome needs to be followed by the pediatrician, in addition to the cardiologist, pulmonologist, physiotherapist and speech therapist.
Children with Down Syndrome also present a delay in psychomotor development and begin to sit, crawl and walk, later than expected. In addition, it usually has a mental retardation that can range from mild to very severe, which can be verified through its development. Find out how is the development of the baby with Down.
The person with Down syndrome may still have other health problems like diabetes, cholesterol, triglycerides, like anyone else, but may still have autism or another syndrome at the same time, although it is not very common.