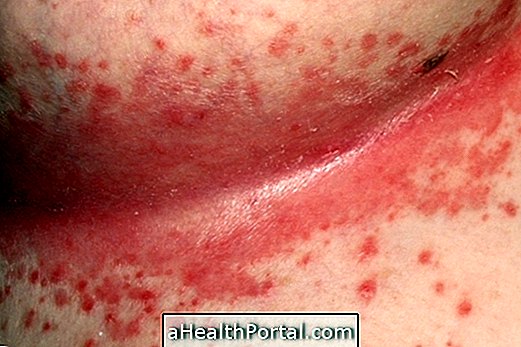
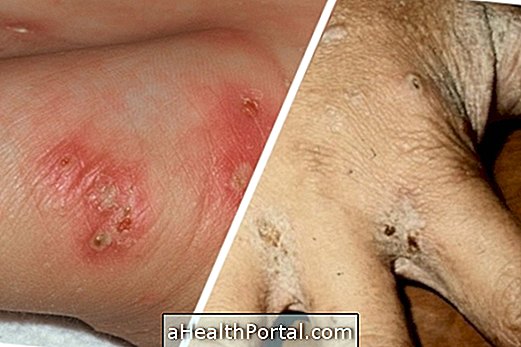
Mycoplasma genitalium is a sexually transmitted bacterium that can infect the female and male reproductive systems and cause persistent inflammation of the uterus and urethra in the case of men. The treatment is done with the use of antibiotics, which should be used by the infected person and his partner to prevent new infections, in addition to using condoms.
This bacterium causes symptoms such as pain and burning when urinating, and is identified through urinalysis or analysis of secretions of the penis or uterus, indicating the presence of Mycoplasma sp . Treatment should be started as soon as the disease is identified, as it can lead to problems such as infertility and inflammation in the prostate.


Symptoms of Mycoplasma genitalium
Infection with Mycoplasma genitalium can lead to the presence of aqueous discharge in the penis or bleeding outside the menstrual period, usually after intimate contact, in the case of women. Other characteristic symptoms of infection by this bacterium that can occur in both men and women are:
- Pain and burning when urinating;
- Pain when having intimate relationships;
- Pain in the pelvic region;
- Fever.
In the presence of these symptoms, the gynecologist or urologist should be sought to perform tests that can identify the cause and initiate appropriate treatment, avoiding future complications.
The diagnosis of Mycoplasma genitalium infection is made by analyzing the symptoms and signs of recurrent inflammation of the urethra and uterus described by the patient and evaluated by the physician, in addition to a microbiological examination of the urine or a penile or vaginal discharge, in which it is identification of the bacterium, which is usually described in the report as Mycoplasma sp ., which represents infection by any type of Mycoplasma.
Possible Complications
If the infection is not quickly identified and treated, there may be some complications in both men and women. In men, in addition to causing inflammation of the urethra, Mycoplasma genitalium infection, when left untreated can lead to inflammation of the testicles and prostate. In women, untreated infection can result in inflammation of the uterus, cervicitis, urethritis, ectopic pregnancy, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
In addition, non-treatment of Mycoplasma infection can result in premature labor, infertility and chronic pelvic pain. Know the top 10 causes of pelvic pain.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment of infection with Mycoplasma genitalium is done with antibiotics according to the medical recommendation and aims to eliminate the bacteria. Treatment should be done by both the infected person and his or her partner, since the partner may have been exposed.
During treatment it is also recommended to avoid having intimate contact to ensure that a new infection will not happen. In addition, it is important to remember that symptoms such as pain when urinating or having intimate relationships may be indicative of Sexually Transmitted Diseases, so it is important to consult your doctor. Learn all about STIs.
The treatment of infection by this bacteria should be started as soon as possible and must be done according to the medical recommendation, as Mycoplasma genitalium has been reported to be becoming resistant to several antibiotics, which makes it difficult to treat. It is also important to use condoms to avoid contamination by this microorganism