Psittacosis, also known as Parrot Fever, is a rare type of pneumonia, transmitted by chlamydial bacteria present in birds, which when manifested in humans produces symptoms such as fever, chills, headache, blocked airways, coughing and nasal bleeding, enlargement of the spleen and lung lesions.
Birds such as parrots, pigeons and macaws are the natural reservoirs of the disease, which is transmitted to humans via the respiratory tract, through aspiration of feather dust or by direct contact with objects contaminated with the feces or urine of infected animals.
Psittacosis is a highly contagious disease.
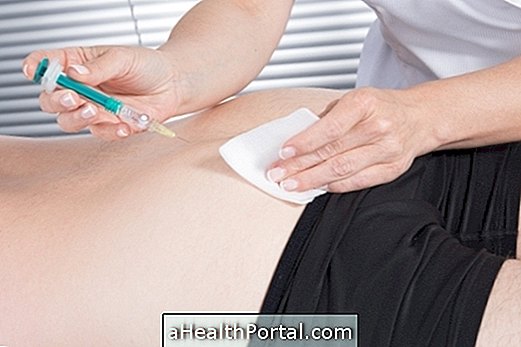
The diagnosis is made through blood tests and treated with the use of tetracyclines for at least 10 days, but symptoms begin to regress after 2 days of the start of treatment.
Bird owners can protect themselves by avoiding contact with feather dust and sick birds' cages, while maintaining a healthy diet and good hygiene at the bird farm.