Colitis is an inflammation of the vagina or cervix that generates symptoms such as small discharge and vaginal odor. It is only identified on a gynecological examination, such as a pap smear, or a schiller test in the doctor's office.
This vaginal inflammation is not considered a sexually transmitted disease and can be caused by different fungi, bacteria and protozoa like Trichomonas or Gardnerella, for example. Get to know other micro-organisms that cause colitis here.
Main symptoms
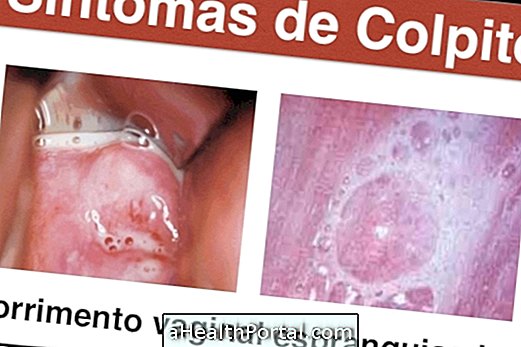
The main symptom of colpitis is whitish or grayish vaginal discharge, similar to milk, which can sometimes be bullous, although this is not very common. Many women report the bad smell in the intimate region, similar to the smell of fish, which tends to become even more evident after intimate contact.
Usually there are no signs of local inflammation such as redness or swelling of the affected tissues and when they are present you should identify which bacteria or fungus is causing the disease to be able to adjust the treatment.
Click here to know How the doctor confirms that it is Colpite
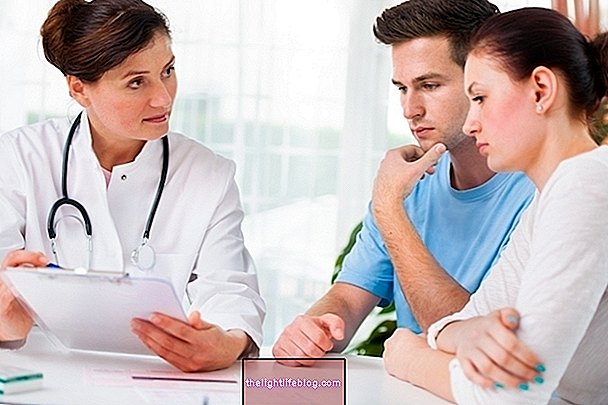
The gynecologist or urologist may arrive at the diagnosis of colpitis by observing the intimate region, signs observed and through tests that can confirm the microorganisms that cause the inflammation.
The most indicated exams are:
- PH test: > 4.7
- 10% KOH Test: Positive
- Fresh blood test : Increased indicator cells, rare leukocytes
- Gram test: Decreased lactobacillus, absence of leukocytes and presence of gram negative and cocci.
The pap smear is not the most indicated for the diagnosis of colpitis because it is not very specific and may not indicate the presence of infection.
What can cause Colpite
Inflammation of the vagina and cervix is more frequent in women living in tropical and developing countries such as Brazil, and the hottest regions are the most affected. In addition, hygiene habits such as using vaginal douche often or not wearing cotton undergarments favor the installation of disease-causing fungi and bacteria.
Another possible cause is getting more than 4 hours with the absorbent inside the vagina. In addition to the hormonal changes, use of antibiotics, having intimate contact during menstruation, having a new partner or keeping intimate with several different partners also contribute to the installation and permanence of colpite.Treatment
The treatment is medicated and if, in addition to inflammation, there is some harmful microorganism in the vagina, it should also be eliminated through the use of antibiotics in the form of tablets or cream to apply directly to the intimate parts. Find out which remedies are listed here.
For treatment to be effective it is also important to adopt some strategies such as wearing only cotton underwear, not wearing pants every day, just washing the external region of the vagina and always use condoms in all sexual relations, even if you choose another method contraceptive, since the best barrier to protection against gynecological diseases is the condom.