Toxoplasmosis, commonly known as cat disease, is an infection caused by a protozoan called Toxoplasma gondii . The disease is transmitted by ingestion of contaminated food, unpasteurized milk, blood transfusion or mother-to-child transmission, when pregnant women are infected and do not treat the disease.
This infection causes no symptoms in most people, but some can develop severe forms of the disease, especially pregnant women and people with compromised immunity, with serious consequences such as blindness, seizures and death. However, toxoplasmosis has a cure and its treatment is done through the use of antibiotics.

How transmission occurs
Transmission of toxoplasmosis can occur through:
- Consumption of raw and poorly sanitized foods that are contaminated with cat feces;
- Consumption of raw or undercooked meat from contaminated animals, mainly pigs, cattle and sheep;
- Ingestion of contaminated water;
- Mother-child contamination, when the pregnant woman passes the protozoan to the baby.
Toxoplasmosis is not transmitted directly from person to person, and the first symptoms appear about 5 to 20 days after the infection.
Main symptoms
Toxoplasmosis usually does not cause symptoms in most people, but may occur:
- Hindrances through the body, especially in the neck region;
- Fever;
- Muscle and joint pain;
- Tiredness;
- Headache and sore throat;
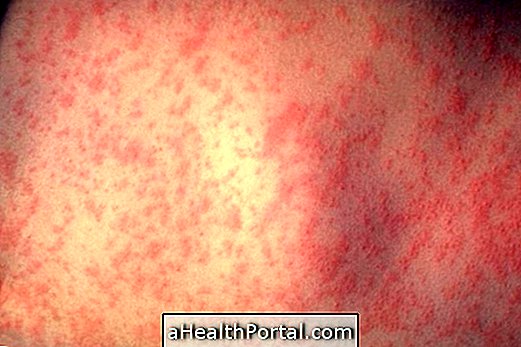
- Red spots on the body;
- Difficulty in seeing.
Symptoms most commonly appear in people with weakened immune systems, such as those who get cancer chemotherapy, transplanted, HIV positive, or in women who get the infection during pregnancy.
In more severe cases, toxoplasmosis can impair the functioning of organs such as the lungs, heart, liver and brain, and usually the symptoms of severe form are severe tiredness, drowsiness, delirium, and decreased strength and body movements. Learn more about the symptoms and when you suspect toxoplasmosis.

Types of toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis can spread through the bloodstream, occurring in a widespread or localized way in the lymph nodes or in some organs such as eyes. Learn the differences between the major types of toxoplasmosis. Some of the major types include:
1. Ocular toxoplasmosis
Ocular toxoplasmosis is when the infection reaches the eye and affects the retina, causing inflammation that can lead to blindness if left untreated. This disease can affect both eyes, and the damage in vision may be different for each eye.
The main symptoms of ocular toxoplasmosis are decreased vision, redness and pain in the eye, and vision with black spots.
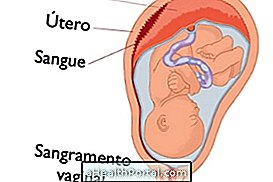
2. Congenital toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy causes congenital toxoplasmosis, which is when the baby is infected by this disease still in the mother's womb. Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy can lead to serious consequences, such as:
- Fetal malformations;
- Low weight at birth;
- Premature birth;
- Abortion;
- Death of the baby at birth.
The newborn with congenital toxoplasmosis may have severe symptoms, which include:
- Strabismus, which is when one eye is not in the right direction;
- Inflammation of the eyes that develops into blindness;
- Intense jaundice, which is yellowish skin and eyes;
- Liver enlargement;
- Pneumonia;
- Anemia;
- Carditis;
- Convulsions;
- Deafness;
- Mental retardation.
The severity of the consequences of toxoplasmosis for the baby depends on the time of the pregnancy in which there was the contagion and the early onset of the treatment. Learn more about the risks of toxoplasmosis in pregnancy.
How is the treatment done?
Toxoplasmosis has a cure and its treatment is done with the use of antibiotics, which vary according to the type and severity of the infection. Longer treatment is indicated in cases of pregnancy, congenital toxoplasmosis and individuals with immune deficiency, such as people with AIDS or Hodgkin's disease.
Treatment of toxoplasmosis should be started as soon as the disease is identified. The diagnosis is made through a blood test that identifies the presence of IgG and IgM antibodies in the body, which are produced to combat the protozoan that causes the disease.


Prevention of toxoplasmosis
Prevention of toxoplasmosis can be done through care such as:
- To sanitize fruits and vegetables that will be consumed raw : one must use water and sanitary water, in proportion of 1 tablespoon of sanitary water for 1 liter of water. The vegetables should be immersed in this mixture for 30 minutes and then rinsed under running water;
- Consume potable, filtered or mineral water;
- Cook the meat well and avoid eating unheated meat in restaurants;
- Avoid contact with unknown cats and wash your hands thoroughly if you touch animals you do not know.
People who have domestic animals should take them to the veterinarian for tests that identify the presence of toxoplasmosis, preventing the transmission of this disease to humans. Learn more tips to protect yourself.