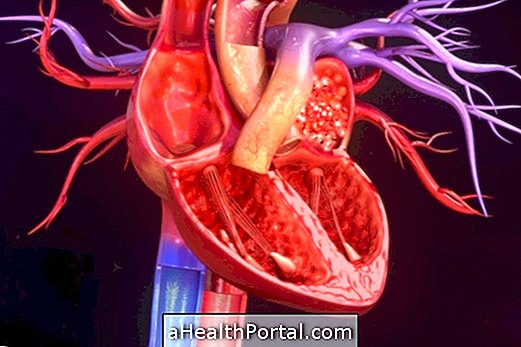
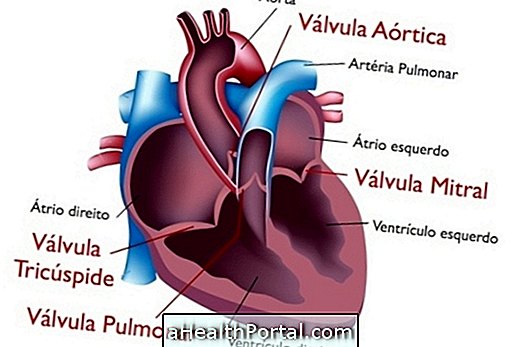
Cardiovascular diseases are a set of problems that affect the heart and blood vessels, causing diseases and serious complications to the health of the person, such as heart attack, heart failure, arrhythmias, stroke or other types of changes in blood circulation.
These diseases usually affect more men than women, at ages older than 50 years. The risk of developing cardiovascular disease is much higher in people with high cholesterol, diabetes, high blood pressure and unhealthy lifestyle, such as sedentary lifestyle, obesity or high levels of stress, so it is often possible to prevent these diseases.
It is important that these diseases be prevented because, in addition to causing various uncomfortable symptoms, such as shortness of breath, chest pain and swelling in the body, they are the leading cause of death worldwide. Understand how the cardiovascular system works and why it is important for your health to function.
What are the types
Two types of cardiovascular diseases can be considered: those with symptoms such as angina or cardiac arrhythmias and those with atherosclerosis or hypertension, which usually do not present symptoms. Because they are silent, they are a reason to go to the cardiologist regularly for routine check-ups, especially for those who already have a family history of heart disease.
The most common heart diseases are:
- Hypertension;
- Acute myocardial infarction;
- Angina of the chest;
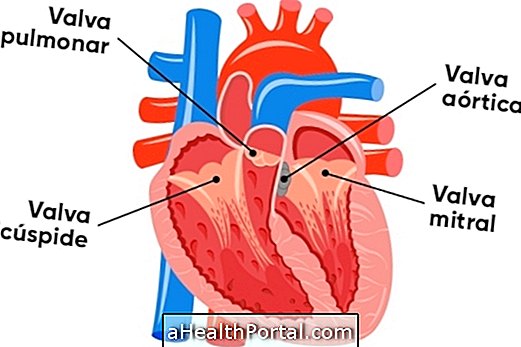
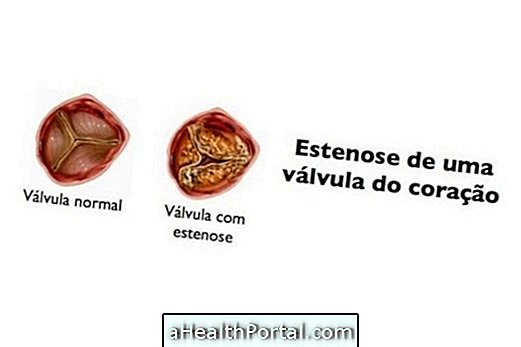
- Heart valve disease;
- Congenital heart diseases;
- Endocarditis;
- Cardiac arrhythmias;
- Myocarditis;
- Tumors in the heart.
Cardiovascular diseases are more common in people over 50 and in the elderly, and may be the result of unhealthy lifelong habits such as poor diet, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, or excessive stress.
Main symptoms
The symptoms of cardiovascular disease are variable, and are usually associated with the type of illness that the person has and the organs most affected, ranging from silent stages to those in which the person already has severe limitations, such as difficulty in breathing, chest pain, fainting, changes in heart rate, or swelling in the legs.
Symptoms usually only start to appear at stages where the disease is already present, making it difficult to prevent it, and it is very important to carry out complementary medical examinations that allow the correct diagnosis and start treatment as soon as possible, both to relieve symptoms as to avoid the worsening of the picture. Learn more about identifying symptoms that indicate heart disease.

Causes of cardiovascular diseases
The causes of cardiovascular diseases are the most diverse, but may be related to the individual's lifestyle and diet, and may be:
- Age: individuals over 50 years of age are at higher risk for cardiovascular disease;
- Gender: Men are usually more affected by cardiovascular problems;
- Family history of cardiovascular diseases;
- Cigarette;
- High cholesterol;
- Hypertension;
- Obesity;
- Sedentary life;
- Diabetes;
- Oral contraceptives;
- Bad eating habits;
- Stress.
All these risk factors facilitate the formation of lesions and the accumulation of plaques of fat in the blood vessels, called atherosclerosis, in addition to other changes in blood circulation, responsible for cardiovascular diseases.
How to treat
The treatment of cardiovascular diseases should be indicated by the cardiologist, and its main objective is to prevent the worsening of the problem. Thus, in addition to changes in lifestyle, to make them healthier, medications may be indicated to control symptoms, blood pressure, heart rate or blood sugar and cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of injury to the body .
Some examples of commonly used drugs include antihypertensives (eg Captorpil, Enalapril, Losartan, Hydrochlorothiazide), diuretics (eg, Furosemide, Spironolactone), beta blockers (eg Propranolol, Carvedilol, Metoprolol), anticoagulants e.g., Mareven, Coumadin, Rivaroxaban) or statins (eg, Simvastatin, Atorvastatin).
How to do the prevention
The prevention of cardiovascular diseases is the best way to avoid the onset of these diseases. Some tips to prevent cardiovascular disease can be:
- Stop smoking;
- Control of blood pressure, sugar levels and fat in the blood, with the use of medicines and follow the doctor's instructions;
- Eating healthy, avoiding fats and eating more vegetables, fruits and cereals;
- Practice physical exercise regularly, at least 30-60 minutes, 3-5 times a week;
- Avoid consumption of alcoholic beverages;
Also, for people who are overweight, it is recommended to lose weight as it is proven that the accumulation of fat is very harmful to cardiovascular health. Check out nutritionist guidelines on how to make a healthy diet to lose weight.