Endometriosis is a disease in which the tissue lining the inside of the uterus, known as the endometrium, grows elsewhere in the body beyond the uterus. One of the most affected sites is the gut, and in those cases the woman may have blood in the stool.
This is because the endometrial tissue in the intestine makes it difficult for stool to pass, which causes irritation of the intestinal wall and bleeding. However, the presence of blood in the stool may also be caused by other problems such as hemorrhoids, fissures, or even colitis, for example. See other common causes of blood in the stool.

Thus, endometriosis is usually only suspected when the woman already has a history of the disease elsewhere or when other symptoms appear, such as:
- Bleeding that worsens during menstruation;
- Constipation with very painful cramps;
- Persistent pain in the rectum;
- Abdominal pain or cramps during intimate contact;
- Pain when stool.
In many cases, the woman has only 1 or 2 of these symptoms, but it is also common for all symptoms to appear over several months, which makes diagnosis difficult.
However, if endometriosis is suspected, it is important to consult a gastroenterologist to identify if there is any change and to start treatment appropriately.
How To Tell If It Really Is Endometriosis
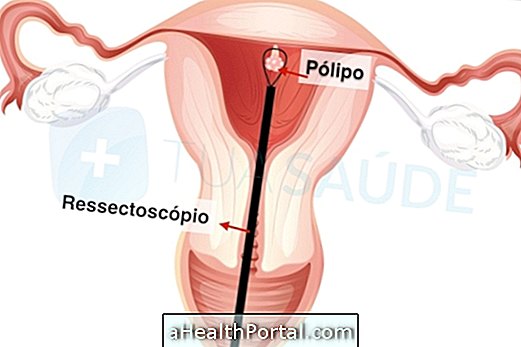
To confirm the presence of endometriosis the doctor can request tests such as colonoscopy or even transvaginal ultrasonography. If the diagnosis is made, the doctor may also order a laparoscopy to know the severity of the endometriosis and which organs are affected. Learn more about exams for endometriosis.
If endometriosis is not confirmed, the doctor may order other tests to identify what is causing bleeding in the stool.
How to treat endometriosis
Treatment for endometriosis may vary depending on the affected sites, however, it is almost always initiated with the use of hormonal remedies, such as contraceptives or anti-hormonal remedies, such as Zoladex, to control the growth of endometrial tissue.
However, when the symptoms are very intense or when the woman wants to become pregnant and therefore does not want to use hormonal remedies, it can also be considered surgery, in which the doctor removes excess endometrial tissue from the affected organs. Depending on the degree of endometriosis, there are organs that may need to be completely removed, such as the ovaries, for example.
Understand better how endometriosis treatment is done and what options are available.