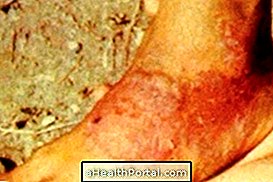
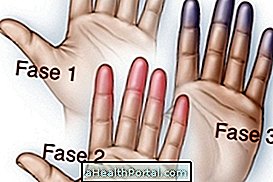
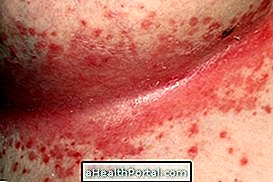
Melanoma is a type of malignant skin cancer that develops very fast and therefore can easily affect other organs through metastases when treatment is not started quickly.
This type of cancer begins in melanocytes, which are the skin cells that produce melanin, the substance that gives color to the skin. Thus, melanoma is more frequent when there are frequent lesions in these cells, which can happen due to prolonged exposure to the sun and, mainly, sunburn.
Unlike most types of cancer, melanoma appears on the skin and, therefore, can be easy to identify early, facilitating treatment and increasing the chances of cure. Therefore, it is necessary that the person is attentive to changes in the skin, especially appearance or growth of signs, making a complete inspection at least every 1 or 2 months.
Learn to identify a blemish on the skin that may be melanoma.

Types of Melanoma
The type of melanoma varies according to the place of appearance and its form of development, and the main 4 types are:
- Extensive superficial melanoma: is the most common type of melanoma that develops initially in the most superficial cells of the skin, taking more time to reach other organs;
- Acral lentiginous melanoma: initially reaches the most superficial layers of the skin, especially of the palms of the hands, soles of the feet and nails, being the melanoma more common in blacks, Asians and Hispanics;
- Lentigo malignant melanoma: observed in areas that are more exposed to the sun, such as face, neck and back of the hands, usually in the elderly;
- Nodular melanoma: is the most aggressive type of melanoma, reaching other body sites from the beginning. It starts as a high black, bluish or red-blue spot.
The easiest types to heal completely are those that develop in the most superficial layers of the skin, since diagnosed at a less advanced stage. When the cancer begins to reach deeper layers or other organs, the treatment is more difficult and the chances of cure are lower.
In rare cases, melanoma may also develop in the mucous membranes of the vagina, esophagus, anus or intestines and also in the eyes, in this case called orbital melanoma.
Does Melanoma have a cure?
Melanoma has a high cure rate when it has not yet developed into other parts of the body. Therefore, it is very important to observe signs and skin spots frequently, looking for changes.
In addition, patients who have had some type of skin cancer or who have direct relatives with this history should go to the dermatologist because they present a greater risk.

Who has a higher risk of having melanoma
In addition to sun exposure and frequent sunburn, melanoma can also be triggered by any other type of exposure to UV rays, such as tanning chambers, for example. This is because this type of light is able to penetrate the cells, and can cause malignant changes that lead to cancer growth.
However, melanoma can appear anywhere on the body, even if protected from UV light, so even though it is more rare, it can also develop in people who avoid sun exposure, being related to family, genetic and environmental factors.
Some factors that appear to increase the risk of developing melanoma include:
- Have blue eyes, fair skin and blonde hair;
- Difficulty in tanning;
- Have ease to get freckles;
- Have a history of skin cancer in the family;
- Having a disease that affects the immune system.
People with 1 or more of these factors should make regular consultations with the dermatologist to make a complete assessment of the skin in order to identify possible changes that may be an early sign of cancer.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for this type of cancer should be guided by an oncologist or dermatologist, depending on the degree of development it may be necessary to only have surgery to remove the tumor and achieve healing, or other treatments such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy may be necessary to eliminate cancer cells that remain on the skin, even after the stain has been removed.
If metastases are present, chemotherapy and radiotherapy should be started as soon as possible. However, success rates are relatively low, as metastases arise in later stages of cancer.
Learn more about the different ways of treating melanoma.