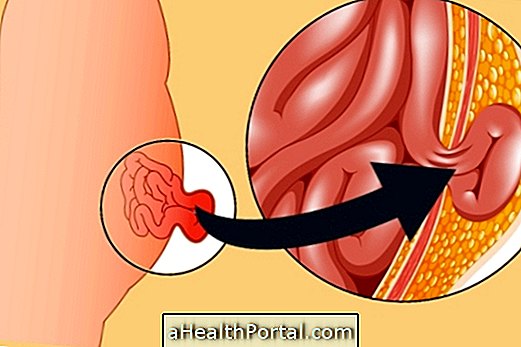
Buerger's disease, also known as thromboangiitis obliterans, is an inflammation of the arteries and veins, legs, or arms that causes pain and changes in the temperature of the skin on the hands or feet due to reduced blood flow.
Buerger's disease usually occurs in men who smoke between the ages of 20 and 45, because the disease is related to cigarette toxins.
There is no treatment for Buerger's disease, but some precautions, such as quitting smoking and avoiding temperature variations, help reduce your symptoms.
Photo of Buerger's disease
Treatment for Buerger's disease
Treatment for Buerger's disease should be followed up by the general practitioner, but it is usually started by reducing the amount of cigarettes smoked per day until the person quits smoking, since nicotine promotes the worsening of the disease.
In addition, the individual should also avoid using nicotine patches or drugs to stop smoking, and should ask the doctor to prescribe drugs without this substance.
There are no remedies to treat Buerger's disease, but some care for Buerger's disease includes:
- Avoid exposing the affected region to cold;
- Do not use acidic substances to treat warts and calluses;
- Avoid cold or heat sores;
- Wear closed and tight shoes;
- Protect feet with cushioned bandages or use foam boots;
- Take walks 15 to 30 minutes twice a day;
- Raise the head of the bed about 15cm to facilitate blood circulation;
- Avoid drugs or drinks with caffeine, as they cause narrowing of the veins.
In cases where there is no complete blockage of the veins, bypass or nerve-removal surgeries can be used to prevent spasm of the veins, thereby improving blood circulation.
Physiotherapeutic treatment for Buerger's disease does not cure the problem, but it helps improve blood circulation through exercises and massages done at least 2 times a week.
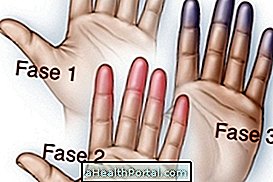
Symptoms of Buerger's Disease
Symptoms of Buerger's disease are related to decreased blood circulation and include:
- Pain or cramp in the feet and hands;
- Swelling in feet and ankles;
- Cold hands and feet;
- Skin changes in affected areas with ulcer formation;
- Variations in skin color, from white to red or purple.
Individuals with these symptoms should consult a general practitioner or cardiologist to diagnose problems by ultrasound and initiate appropriate treatment.
In severe cases of the disease, or when patients do not stop smoking, gangrene may appear in the affected limbs and amputation is necessary.
Useful links:
- Raynaud: When the fingers change color
- Atherosclerosis
- Treatment for poor circulation