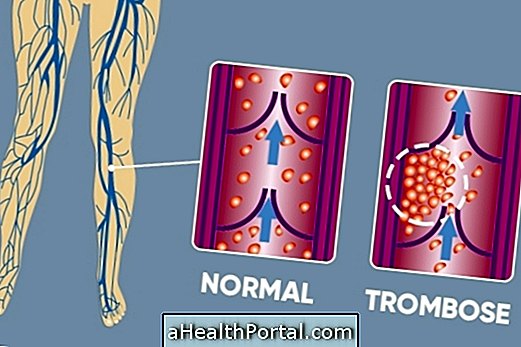
Thrombosis is characterized by the formation of blood clots within veins or arteries, preventing normal blood circulation, causing pain and swelling in the legs or arm, for example. Typically, thrombosis occurs in people who have varicose veins, who sit or lie down for a long time, such as a plane ride, hormone intake, during pregnancy or as a result of surgery. Learn to correctly identify the symptoms of thrombosis.
Thrombosis may be superficial or deep, such as deep venous thrombosis. However, in any case treatment with medication should be urgent because the blood clot can flow through the bloodstream lodged in organs such as the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism, or in the brain, generating cerebral thrombosis, for example, serious situations that can even lead to death.
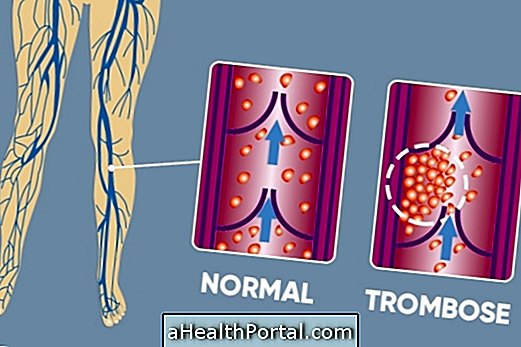
Symptoms of each type of thrombosis
There are some types of thrombosis, depending on where the vessels become clogged, and the major type if symptoms they cause are:
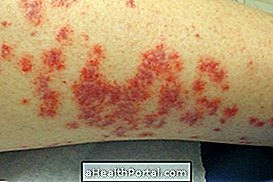
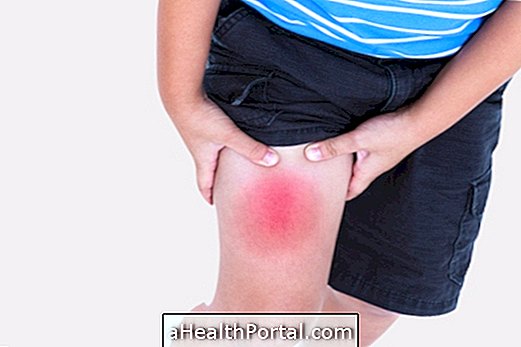
- Thrombosis in the legs : Swelling, redness, and heat in the affected area that worsen over time, usually with pain or feeling of heaviness, and the skin may become stiff. Although thrombosis in the legs is more common, since it is where the blood can travel more slowly, it can also arise in any other place, such as arms or hands, for example.
- Pulmonary embolism : shortness of breath, coughing and tiredness, which can worsen and cause intense difficulty breathing;
- Cerebral thrombosis : Stroke symptoms, such as tingling or paralysis on one side of the body, crooked mouth, difficulty speaking or changes in vision, for example. Understand how cerebral thrombosis happens and how to treat it.
However, in some cases, depending on the size of the blood clot and the blood vessel where it is housed, it may not generate any symptoms. In addition, there is thrombophlebitis, which is the partial closure of a superficial vein, causing localized swelling and reddening of the affected vein, which causes a lot of pain upon palpation.
In the presence of signs and symptoms that indicate thrombosis, the medical emergency service must be sought immediately, so that the doctor can make a clinical evaluation and, if necessary, request an examination such as ultrasound or tomography. This is why it is necessary to start a quick treatment with anticoagulant drugs, such as Heparin, for example.
Cure and how treatment is done
Thrombosis has a cure, and its treatment has two fundamental goals, which are to prevent clot growth and prevent existing clots from loosening. These goals can be achieved through the use of anticoagulant medications, such as Heparin and Warfarin, under the guidance of the vascular surgeon or cardiologist.
In some cases, it is necessary to stay in the hospital to adjust medication doses and perform tests more quickly. After the initial period, it will be recommended to take some care, such as avoid sitting down with your legs down and always wear elastic compression socks, such as Kendall socks, for example.
See more details on treatment options for thrombosis.
What to do to prevent thrombosis
Prevention of thrombosis can be done through a healthy diet, good hydration and regular physical exercise, which improves blood circulation, decreases inflammatory processes and prevents the accumulation of fat plaques in blood vessels.
In cases of surgery, it is important that the doctor indicates, when indicated, medicines to prevent thrombosis, such as prophylactic heparin. In addition, physiotherapy can help you stay active during this period, even when you have to lie down with your feet, for example. This type of movement is important to improve blood circulation, since venous stasis favors the formation of thrombi.
In people who have varicose veins, circulatory problems or remain sitting or standing for a long time at work, it is recommended to use medium compression elastic stockings. Also, in situations of standing still for a long time, such as bedridden people, who sit too much time or during a trip, for example, are advised to move around in regular periods.
When traveling, the person should get up every hour and walk a little, in order to facilitate blood circulation. Here are some other tips that can help improve your trip:

Who has more risk
Some risk factors for the development of thrombosis are:
- Family history;
- Obesity;
- Pregnancy and childbirth;
- Blood disorders such as thrombophilia. Understand more about this condition that increases the risk of thrombosis;
- Injuries or surgeries in the legs or feet;
- Use of drugs that interfere with coagulation;
- Very long rest period, whether lying or sitting;
- Age, the risk increases to double for each addition of 10 years from 20 years of age.
The more risk factors an individual has, the more likely he or she will develop thrombosis.


Thrombosis in pregnancy
The risk of thrombosis increases greatly in pregnancy because the blood's ability to coagulate increases, especially at the end of gestation, as a natural way of surviving childbirth. If the mother observes the symptoms of thrombosis, she should immediately go to the hospital for treatment to begin, as this is a serious situation.
Treatment of thrombosis during pregnancy can be done with injectable Heparin, since warfarin is contraindicated in pregnancy because it is harmful to the baby. It is important to note that when a woman suffers an episode of thrombosis during pregnancy, she should continue the treatment until 3 or 6 months after the baby is born. In addition, she is at greater risk of developing other thrombosis in life and should therefore be prevented. Learn how to identify and treat thrombosis in pregnancy.