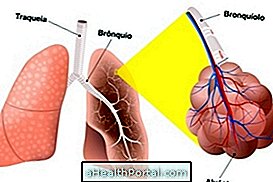
The treatment for a lung infection varies according to the microorganism that is causing this infection. Thus, if it is being caused by a virus, the infection is treated with an antiviral, if it is caused by bacteria, an antibiotic is used.
Usually treatment is faster in the case of bacteria because there are many antibiotics for different types of bacteria, while there are only antivirals for some types of virus and therefore the virus needs to be eliminated by the body.
The antibiotics most frequently prescribed by the penumologist include:
- Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid;
- Clarithromycin;
- Azithromycin;
- Cefuroxime;
- Ciprofloxacin.
In addition, there may still be lung infections caused by fungi, and in such cases, the doctor may advise the use of an antifungal tablet, such as Itraconazole or Fluconazole, for example. Fungal infections of the lung are usually more common in people with weakened immune systems and therefore may take longer to heal.
Internment is usually only necessary in the case of a very advanced infection in which the drugs need to be administered directly into the vein for a faster effect. These cases are more frequent in the elderly or children, because they have a more fragile immune system.
Look at the symptoms of pneumonia caused by viruses and pneumonia caused by bacteria.
When to start treatment
The treatment is most effective when the pulmonologist identifies the cause of the infection and for this reason, various tests such as a blood count, X-ray or sputum examination may be ordered before starting the treatment. However, some doctors may also indicate the use of an antibiotic even before the test results, since bacterial infection is the most common.
After the results, if it is discovered that the infection in the lung is being caused by a virus or a fungus, the antibiotic can be stopped and a new treatment is initiated, with a more appropriate remedy to eliminate the responsible microorganism.
How to speed recovery
The remedies for lung infection are very important to aid in healing, however, there are some care that help to strengthen the body and accelerate recovery, such as:
- Drink 2 liters of water per day to keep the body well hydrated and help eliminate lung secretions;
- Avoid leaving the house during treatment, to avoid abrupt changes in temperature;
- Do not use cough medicine without the doctor's advice, as they prevent the secretions from flowing out;
- Drip physiological saline drops into the nostrils to help eliminate secretions and facilitate breathing;
- Sleep with a high pillow to ease sleep and keep your nose from getting clogged.
It is further advised to wear a mask and not cough or sneeze close to other people, especially in the case of a virus infection, to prevent transmission of the disease.
Feeding can also help a lot in recovery, so check out our nutritionist's tips on what to eat during treatment:

These care are even more important in cases of pulmonary virus infection, because as there are no antivirals for all these types of microorganisms, it is necessary to help strengthen the immune system so that it can eliminate them faster. See more natural options to strengthen the immune system.
Possible Complications
When the lung infection is not properly treated, it can progress to pneumothorax, abscess, respiratory failure and even sepsis, with a risk of death.
Signs of improvement
Signs of improvement usually appear up to 3 days after initiation of treatment and include fever reduction, cough suppression, and reduced secretion.
Signs of worsening
Worsening signs usually arise when treatment is not effective or when it is not started quickly, and includes increased fever, difficulty breathing, and coughing up phlegm with blood, for example.