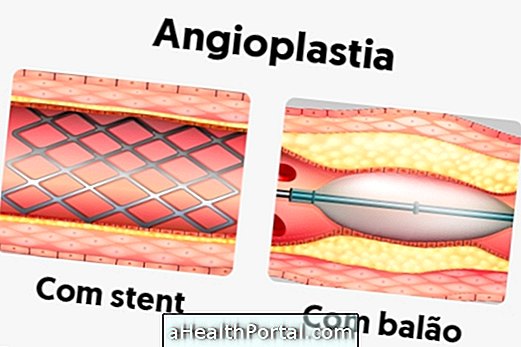
Coronary angioplasty is a procedure that opens a very narrow heart artery or that is blocked by cholesterol accumulation, improving chest pain and avoiding the onset of serious complications such as infarction.
There are 2 main types of angioplasty, which include:
- Balloon angioplasty : A catheter is used with a small balloon at the tip that opens the artery and makes the cholesterol plaque flatter, facilitating the passage of blood;
- Stent angioplasty : in addition to opening the artery with the balloon, in this type of angioplasty, a small network is left inside the artery, which helps to keep it always open.
The type of angioplasty should always be discussed with the cardiologist, as it varies according to the history of each person, requiring a thorough medical evaluation.
This type of surgery is not considered a risk because it is not necessary to expose the heart, only passing a small flexible tube, known as a catheter, from an artery in the groin or arm to the artery of the heart. Thus, the heart is functioning normally throughout the procedure.
How is angioplasty performed?
Angioplasty is done by passing a catheter through an artery until it reaches the vessels of the heart. For this, the doctor:
- Place a local anesthetic in a groin or arm location;
- Insert a flexible catheter from the anesthetized site to the heart;
- Fill the balloon as soon as the catheter is in the affected location;
- Places a small network, known as a stent, to keep the artery open, if necessary;
- Empty and remove the balloon from the artery and remove the catheter.
Throughout the process, the doctor watches the progress of the catheter through the x-ray to know where it is going and to ensure that the balloon is inflated in the correct location.
Important care after angioplasty
After angioplasty, it is advisable to stay in the hospital to reduce the risk of bleeding and to evaluate the presence of other complications, such as infection. However, it is possible to return home in less than 24 hours. climb stairs in the first 2 days.
Possible risks of angioplasty
Although angioplasty is safer than open surgery to correct the artery, there are some risks such as:
- Clot formation;
- Bleeding;
- Infection;
In addition, in some cases, kidney damage may also occur, because during the procedure a type of contrast is used which, in people with a history of kidney changes, may cause damage to the organ.