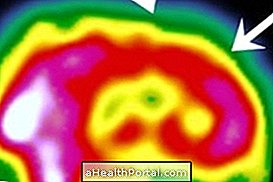
Pulmonary scintigraphy is a diagnostic test that evaluates the presence of changes in the passage of air or blood circulation to the lungs, and is done in two stages called inhalation, also known as ventilation, or perfusion. To carry out the examination it is necessary to use a medicine with radioactive capacities, such as Technetium 99m or Gallium 67, and an apparatus to capture the formed images.
Pulmonary scintigraphy is indicated mainly to aid in the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary embolism, but also to check for other pulmonary diseases, such as myocardial infarction, pulmonary emphysema, or deformities in the blood vessels, for example.
Where is it done?
Pulmonary scintigraphy is done at imaging clinics that contain this device, and can be done free of charge if requested by a physician from SUS, as well as done in private clinics through the health plan or paying the value that is, on average, R $ 800 reais, which varies depending on the location.
What is it for
Pulmonary scintigraphy is used in the following cases:
- Pulmonary thromboembolism, for diagnosis and control of the disease, as the main indication. Understand what is and what can cause pulmonary embolism;
- Observe areas of the lungs where there is no adequate ventilation, a situation called pulmonary shunt;
- Preparation of pulmonary surgeries, by observing the blood circulation of the organ;
- Identify causes of unexplained lung diseases, such as emphysema, fibrosis or pulmonary hypertension;
- Evaluation of congenital diseases, such as malformations in the lungs or blood circulation.
Scintigraphy is a type of examination that is also performed to look for changes in other organs, such as the kidneys, heart, thyroid, and brain, for example, by helping to see various types of changes, such as cancer, necrosis, or infections. Learn more about indications and how the bone scans, myocardial scintigraphy, and thyroid scintigraphy are done.
How is it done and prepared?
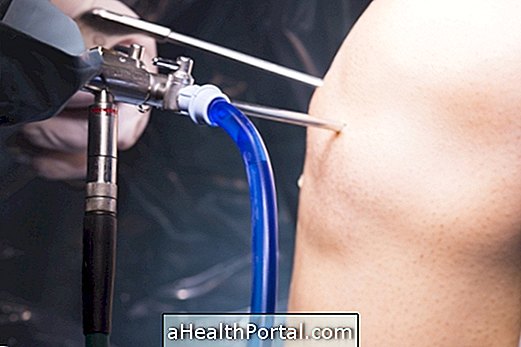
Pulmonary scintigraphy is done in 2 steps:
- 1st stage - Ventilation or Inhalation : it is made with the inhalation of saline containing the radiopharmaceutical DTPA-99mTc that is deposited in the lungs, to then form the images that are captured by the apparatus. The examination is done with the patient lying on a stretcher, avoiding to move, and lasts about 20 minutes.
- Stage 2 - Perfusion : performed with an intravenous injection of another radiopharmaceutical, called MAA labeled with technetium-99m, or in some specific cases Gallium 67, and images of the blood circulation are also performed with the patient lying for about 20 minutes.
No specific preparation or fasting for lung scintigraphy is required, however, it is important on the day of the examination to carry further tests that the patient has done during the investigation of the disease, to help the physician interpret it to interpret the result of a more accurate way.