The HIV test is intended to detect the presence of the HIV virus in the body and should be done at least 30 days after exposure to unsafe sex, such as unprotected sex or contact with blood or secretions from people carrying the virus HIV.
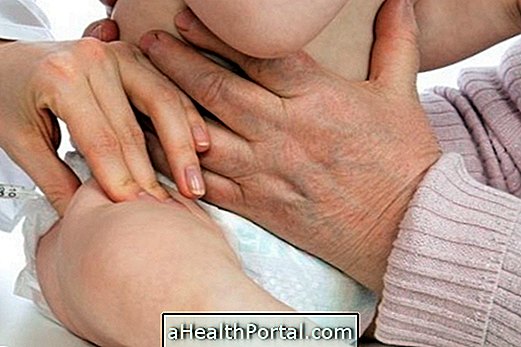
The HIV test is simple and is done primarily through the analysis of a blood sample, but saliva can also be used to check the presence of the virus in the body. All HIV tests research the two types of existing viruses, HIV 1 and HIV 2.
The HIV test should be carried out at least 1 month after the risk behavior, since the immunological window, which corresponds to the time between the contact with the virus and the possibility of detecting the infection marker, is 30 days. the release of a false negative result if the test is performed before 30 days.

How to understand the result
To understand the HIV test result, it is important to check if it is reagent, unreactive or undetermined beyond the indicated values, because usually the higher the value, the more advanced the infection.
HIV blood test
The blood test for HIV is done to identify the presence of the virus and its concentration in the blood, giving information about the stage of infection. The HIV test can be done by means of several diagnostic laboratory methods, the most used being the ELISA method. The possible results are:
- Reagent: It means that the person was and was in contact and became infected with the AIDS virus;
- Non-Reagent: It means that the person is not contaminated with the AIDS virus;
- Undetermined: The test must be repeated because the sample was not clear enough. Some situations that lead to this type of outcome are pregnancy and recent vaccination.
In case of a positive result for HIV the laboratory itself uses other methods to confirm the presence of the virus in the body, such as Western Blot, Immunoblotting, Indirect Immunofluorescence for HIV-1. So, the positive result is even reliable.
In the case of undetermined results, it is recommended that the test be repeated after 30 to 60 days in order to verify the presence or absence of the virus. In such cases, the test should be repeated even if there are no symptoms, such as rapid weight loss, persistent fever and coughing, headache and the appearance of red spots or small sores on the skin, for example. Know the main symptoms of HIV.
HIV Rapid Testing
Rapid tests indicate the presence or absence of the virus and are done by means of a small sample of saliva or a small drop of blood to identify the virus. The result of the rapid test is released between 15 and 30 minutes and are also reliable, with the possible results being:
- Positive: Indicates that the person has the HIV virus but must perform the ELISA blood test to confirm the result;
- Negative: Indicates that the person is not infected with the HIV virus.
Rapid tests are used on the street, in government campaigns in the testing and counseling centers (CTAs), and in pregnant women who begin labor without prenatal care, but these tests can also be purchased over the Internet.
Usually government campaigns use the OraSure tests, which test saliva and the test that can be bought online in online pharmacies abroad is Home Access Express HIV-1, which is approved by the FDA and uses a drop of blood.
When you can give false negative result
The false negative result may occur when the person was tested within 30 days after the risk behavior that may have been unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing of disposable needles and syringes, or puncture with contaminated cutting such as knives or scissors, for example . This is because the body can not produce sufficient amounts of antibodies so that the presence of the virus is indicated in the examination.
However, even if the test was performed 1 month after the risk behavior, the body may take up to 3 months to produce sufficient antibodies against the HIV virus and the result is positive. Thus, it is important that the test be repeated 90 and 180 days after the risk behavior to confirm the presence or absence of the HIV virus in the body.
Basically whenever a result is positive there is no doubt that the person has HIV, while in the case of a negative result, it may be necessary to repeat the test because of the false negative. However, an infectologist may indicate what to do in each case.