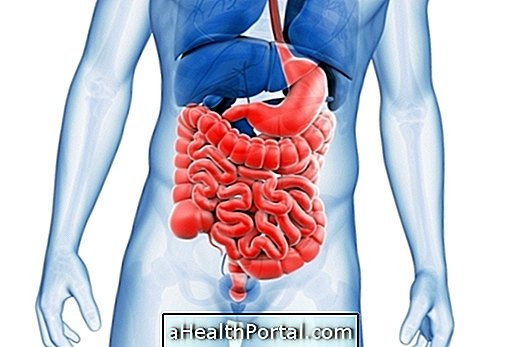
Hepatic elastography is an examination used to evaluate liver fibrosis, which reflects health and liver damage caused by chronic liver disease, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis and the presence of fat.
This test is quick, painless and requires no needles or cuts, and can also be used to diagnose diseases, often replacing biopsy.
However, this technology was only incorporated into the SUS in October 2015, and therefore the examination is still rare in the public health network, but it is possible to find it more easily in private clinics, with prices varying around 1000 reais
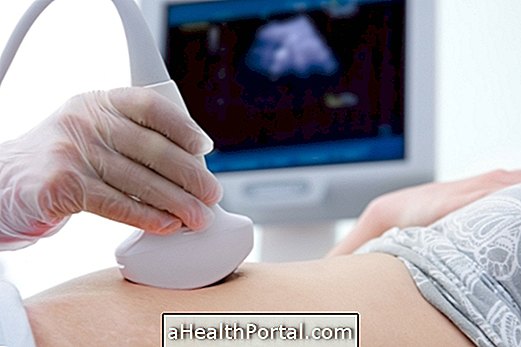
How is the exam done?
The liver elastography lasts on average of 5 to 10 minutes, and no preparation or fasting is necessary before the procedure. It may be called transient ultrasonic or ARFI, depending on the device that is used.
The examination is similar to ultrasound, where the patient lies on his back and with the shirt raised to expose the abdomen, where the doctor inserts the lubricating gel before passing the probe that will generate images on the screen of the device, from the diagnosis and progression of the disease will be assessed.
What diseases do you evaluate?
Hepatic elastography can be used to evaluate the following health problems:
- Hepatitis;
- Fat in the liver;
- Cirrhosis;
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis;
- Hemochromatosis;
- Wilson's disease.
In addition to being used to diagnose and identify the severity of these diseases, this test can also be used to evaluate the success of the treatment because it can assess the improvement or worsening of the liver tissue. See the symptoms of hepatic steatosis, which is fat in the liver.
When the outcome can go wrong
Only a small fraction of the results of elastography tests may be unreliable, a problem that occurs mainly in cases of overweight, obesity and old age of the patient.
In addition, the exam may also fail when done on people with a BMI of less than 19 kg / m2 or when the examiner has no experience in taking the test.
Advantages of Biopsy
Because it is painless and requires no preparation, elastography does not pose risks to the patient, unlike what may occur during a liver biopsy, in which the patient has to be hospitalized for a small piece of the organ to be removed for analyze.
The biopsy usually causes pain at the site of the procedure and hematoma in the belly, and in rarer cases can also cause complications such as hemorrhage and pneumothorax. So, the ideal is to talk with your doctor to evaluate the best test to identify and monitor the disease in question. See how the treatment for liver fat and the degrees of severity of this disease.
Get to know Berardinelli-Seipe syndrome, a disease that decreases the amount of fat in the body, but it increases the liver and causes swollen belly and diabetes.