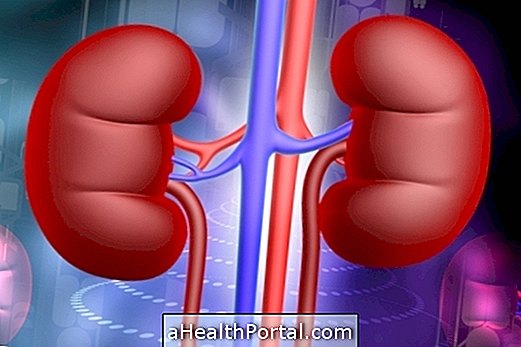
Alport syndrome is a rare genetic disease that causes progressive damage to the small blood vessels that are in the glomeruli of the kidneys, preventing the organ from successfully filtering the blood and symptoms such as blood in the urine and increase in the amount of protein in the examination. urine.
In addition to affecting the kidneys, this syndrome can also cause problems to hear or see, since it prevents the production of a protein important for the functioning of the eyes and ears.
Alport syndrome has no cure, but the treatment helps relieve symptoms and even slows the development of the disease, preventing kidney function from being affected.
Main symptoms
The most common symptoms of Alport syndrome include:
- Blood in the urine;
- High blood pressure;
- Swelling of the legs, ankles, feet and face.
In addition, there are also cases where hearing and vision are affected by the disease, causing difficulty in hearing and seeing.
If proper precautions are not taken, the disease may progress to chronic renal failure and require dialysis or kidney transplantation.
What causes the syndrome
Alport's syndrome is caused by changes in genes that contain instructions for the production of a protein known as type IV collagen. This type of collagen is part of the glomeruli of the kidney and, therefore, when it is not present, the blood vessels of these regions suffer lesions and heal, impairing the function of the kidney.
Likewise, this collagen is also present in the ears and eyes and therefore over time also may appear changes in these organs.
How to confirm the diagnosis
There is no specific test to diagnose Alport syndrome, so your doctor may order several tests, such as urine tests, blood tests, or kidney biopsy to see if there is any change that may be causing the syndrome.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for Alport syndrome is done with the aim of relieving the symptoms, since there is no specific form of treatment. Thus, it is very common to use high blood pressure medicines and diuretics to control blood pressure and prevent the worsening of kidney damage.
In addition, it is also recommended to maintain a low salt diet to avoid excessive kidney function. Here's how to maintain a diet of this type.
In more severe cases where the kidney is severely affected and there is no improvement in symptoms, dialysis or kidney transplantation may be necessary.