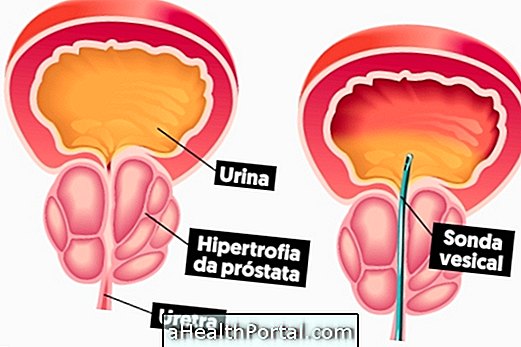
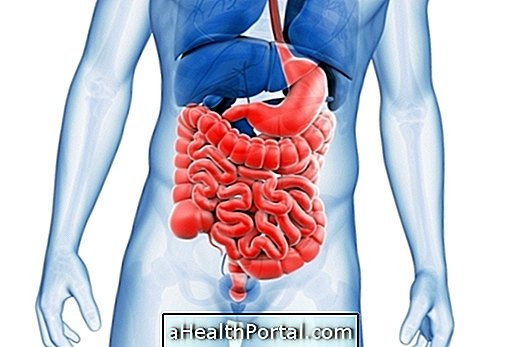
CA 19-9 is a protein released by cells in some tumor types, being used as a tumor marker. Thus, the CA 19-9 exam aims to identify the presence of this protein in the blood and help the diagnosis of some types of cancer, especially advanced pancreatic cancer, in which the levels of this protein are very high in the blood . Here's how to identify pancreatic cancer.
The types of cancer that are most easily identified with this exam include:
- Cancer of the pancreas;
- Colorectal cancer;
- Gallbladder cancer;
- Cancer of the liver.
However, the presence of CA 19-9 may also be a sign of other diseases such as pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, or obstruction of the bile ducts, for example, even people may have a slight increase in this protein without any problems.

When the exam is required
This type of test is usually ordered when symptoms appear that may indicate cancer of the gastrointestinal tract such as frequent nausea, bloated belly, weight loss, yellowing of the skin, or abdominal pain. Usually, in addition to the CA 19-9 exam, other tests may also be done that help to specifically identify the type of cancer, such as the CEA exam, bilirubin, and sometimes liver screening tests. See liver function tests.
In addition, this test can be repeated even after a diagnosis of cancer has already been made and is used as a point of comparison to know if the treatment is having any results on the tumor.
Check out the 12 signs that may indicate cancer and which tests used.
How is the exam done?
The CA 19-9 exam is done as a normal blood test, in which a blood sample is collected and sent to the laboratory for analysis. For this type of clinical analysis, no specific preparation is required.
How to interpret the results
The presence of low amounts of CA 19-9 protein is normal, even in healthy people; however, values higher than 37 U / mL usually indicate that some type of cancer is developing. After the first examination, the test may be repeated several times to check the effectiveness of the treatment, and may indicate:
- The result increases: it means that the treatment is not having the expected result and, therefore, the tumor is increasing, leading to increased production of CA 19-9 in the blood;
- The result remains : it may indicate that the tumor is stable, that is, it does not grow or decrease, and may indicate to the doctor the need to change the treatment;
- The result is less : It is usually a sign that the treatment is being effective and so the cancer is shrinking in size.
In some cases, the result may increase over time even though the cancer is not actually increasing in size, but this is usually more common in the case of radiotherapy treatments.