Eye pain may arise from changes in the ocular surface or in the innermost regions of the eye. In addition to the pain in the eyes people may have other symptoms such as itching and burning which may be due, for example, to problems such as conjunctivitis or sinusitis.
In general, to feel tired eyes and make an effort to see are symptoms that pass after a few hours of sleep and rest, but if the pain is strong or persistent, or if it is accompanied by faults in the vision, an ophthalmologist should be evaluate the cause of the problem.
The pain in the eyes after a blow, entering a cisco or after the attack of an animal with sharp nails, can cause a cornea scratch and in this case there is intense pain in the affected eye, constant lacrimation and difficulty to open the eyes. Here's how to identify and treat a corneal scratch here.
Symptoms
The pain in the eyes usually comes with burning and throbbing pain, with the sensation of being pinched in or around the eye or as if there were some strange object in the eyeball.

In addition, there may be specific symptoms such as:
- Pain when moving the eyes: it can be a sign of speck in the eye or fatigue of the eyes;
- Pain behind the eyes: may be dengue, sinusitis, neuritis;
- Pain in the eye and headache: may indicate vision or flu problems;
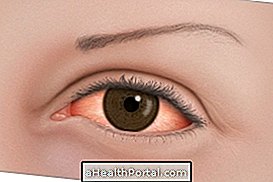
- Pain and redness: is a symptom of inflammation in the eye, such as conjunctivitis;
- Pain on blinking: may be a symptom of stye or speckle in the eye;
- Pain in the eye and forehead: It often arises in cases of migraine.
These symptoms may occur in both the left eye and the right eye, and may also reach both eyes at once.
Common Causes of Eye Pain
The most common causes of eye pain are:
1. Keratitis
It is an inflammation in the cornea that can be infectious or not. It can be caused by viruses, fungi, microbacteria or bacteria, misuse of contact lenses, wounds or strokes in the eye, causing pain, decreased vision, sensitivity to light and excessive eye tearing.
- Treatment: Keratitis has a cure, but treatment should be started as soon as possible, as the disease may spread quickly and can cause blindness. Here's how to deal with it here.
2. Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation on the inner surface of the eyelids and the white part of the eye, causing redness, secretion and swelling in the eyes. It can be caused most commonly by viruses or bacteria, being easily transmitted to other people, or it may be due to some allergy or reaction to an irritating object that came in contact with the eye.
- Treatment: It can be done with the use of analgesic remedies, anti-inflammatories, and antibiotics, in case of bacterial conjunctivitis. See all treatment details here.
3. Misuse of contact lenses
Improper use of contact lenses can cause inflammation and eye infections that lead to pain, redness and itching, as well as more serious problems such as ulcers or keratitis.
- Treatment: The lenses should be used following hygiene recommendations, maximum use time and the shelf life of the product. See the guide on how to choose and wear contact lenses.
4. Dry eyes
The eyes become dry due to several reasons that alter the quality of the tear, responsible for lubricating the eyeball. This problem causes prickling and burning sensation, especially in air-conditioned environments, while cycling or after spending a few hours looking at the computer screen.
- Treatment: Eye drops should be used to aid lubrication of the eyeball. The use of eye drops that reduce redness can be used, but do not treat the cause. In addition, if used indiscriminately and without guidance from the ophthalmologist may mask other vision problems and delay the diagnosis of some more serious problem.

5. Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a multifactorial disease, but its main risk factor is increased pressure in the eyeball, leading to damage to the optic nerve and progressive decrease of vision, if not diagnosed and treated early. As a disease of slow and progressive evolution, in more than 95% of the cases there are no symptoms and no signs of the disease until there is decreased vision. At that moment the person already presents an extremely advanced disease. Therefore, routine consultation with the ophthalmologist is essential to eye health.
- Treatment: Although it has no definitive cure, proper treatment of glaucoma allows the control of symptoms and prevents blindness. See how to know if you have glaucoma.
6. Flu
The presence of infections in the body like flu and dengue can cause symptoms of headache and eye pain, which decrease as the body fights the disease.
- Treatment: You can use strategies such as drinking calming and circulation-enhancing teas, such as ginger, fennel and lavender, putting compresses of warm water on your forehead, using medications such as paracetamol, and staying in a quiet, low-light setting.

7. Sinusitis
Sinusitis is inflammation of the sinuses and usually causes headache and also causes pain behind the eyes and nose. In addition, the patient may present with other symptoms not related to sinusitis, such as sore throat and difficulty breathing, especially in a viral condition.
- Treatment: It can be done with medicines applied directly on the nose or with antibiotic and anti-flu medications. See more on how to identify and treat sinusitis.
8. Dengue fever
The pain in the back of the eyes, accompanied by symptoms such as tiredness and pain in the body may indicate dengue, which is common especially in the summer.
- Treatment: There is no need for specific treatment and can be done with painkillers and medicines to lower the fever. Check all the symptoms to know if it is dengue.
9. Migraines
Migraine causes an intense headache, especially affecting only one side of the face, and sometimes there are symptoms such as lightheadedness and sensitivity to light, needing to wear sunglasses to feel better. In the case of cluster headache pain affects the forehead and only one eye, with intense pain, in addition to tearing and runny nose. In the case of migraine with aura, in addition to the pain in the eyes, flashing lights may appear.
- Treatment: The treatment is always done with medicines against migraine, prescribed by the neurologist.
10. Optic neuritis
It manifests itself through symptoms such as pain when moving the eyes, which can affect only one or both eyes, as well as sudden decrease or loss of vision, and change in color test. The pain can be moderate or severe and tends to worsen when the eye is palpated. It can occur in people who have multiple sclerosis, but can also happen in case of tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, AIDS, childhood viruses such as mumps, chicken pox and measles, and others such as Lyme disease, cat scratch disease, and herpes, for example.
- Treatment: Depending on the cause, it can be done with taking corticosteroids, for example. Learn more about optic neuritis.
11. Diabetic eye neuropathy
In this case it is an ischemic neuropathy which is the lack of irrigation of the optic nerve and does not cause pain. This is a consequence in diabetics who have not kept their blood glucose properly controlled most of the time.
- Treatment: In addition to controlling diabetes, surgery or laser treatments may be needed. See the full list of symptoms, such as treatment and why diabetes can cause blindness.
12. Trigeminal Neuralgia
It causes pain in the eyes, but usually only one eye is affected, abrupt and intense, similar to the sensation of electric shock, besides intense pain in the face. The pain lasts from a few seconds to two minutes, happening soon after, at intervals of a few minutes to the hour, and can occur several times a day. Often the picture goes on for months, even with proper treatment.
- Treatment: The treatment is done with medicines or surgery, know more details here.
When to go to the doctor
You should seek medical help when eye pain is severe or lasts for more than 2 days, if you have decreased vision, autoimmune diseases, or rheumatoid arthritis, or when there is pain, symptoms of redness, tearing, in the eyes and swelling.
Also, while staying at home it is important to avoid places with too much light, computer use and the use of contact lenses to decrease eye irritation and the chances of complications. Here's how to do a massage and exercises that combat eye pain and the tired sight here.