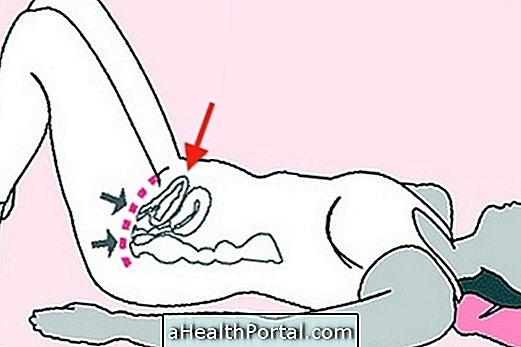
Endometrial cancer is one of the most common types of cancer among women over 60 and is characterized by the presence of malignant cells in the inner wall of the uterus that leads to symptoms such as bleeding between menses or after menopause, pelvic pain, and loss of weight, for example.
The causes of endometrial cancer are still not very well established, however there are some factors that can favor the occurrence of this disease, such as obesity, hormone replacement therapy, arterial hypertension and first premature menstruation.
Ovarian cancer is curable when identified and treated in early stages, and treatment is usually done through surgical procedures.

Symptoms of endometrial cancer
Endometrial cancer can cause some characteristic symptoms, the main ones being:
- Bleeding between normal menstruation or after menopause;
- Menses abundant and more frequent after 40 years;
- Pelvic or colic pain;
- White or clear vaginal discharge after menopause;
- Weight loss;
- Presence of blemishes in uterus.
In addition, if there is metastasis, that is the appearance of tumor cells in other parts of the body, other symptoms related to the affected organ may appear, such as obstruction of the intestine or bladder, cough, difficulty breathing, jaundice and enlargement of the lymph nodes lymphatics.
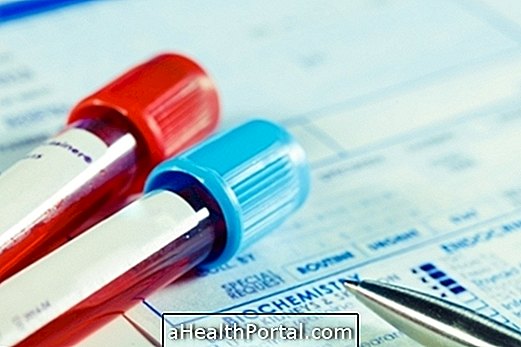
The gynecologist should make the diagnosis of endometrial cancer through examinations such as preventive, endometrial biopsy, curettage, endovaginal ultrasonography or magnetic resonance to guide the appropriate treatment.
Possible causes
The causes of endometrial cancer are still not very well established, but there are some factors that can favor the onset of cancer, such as obesity, high fat diet, high blood pressure, diabetes, endometrial hyperplasia, early menstruation and late menopause.
In addition, endometrial cancer may be favored by hormone therapy, with increased production of estrogen and little or no progesterone production, for example. Other conditions that may favor ovarian cancer include polycystic ovary syndrome, absence of ovulation, genetic predisposition, and family history.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment of endometrial cancer is usually done through surgery, in which the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovary and pelvic lymph nodes are removed when needed. In some cases, the treatment also includes additional therapies, such as chemotherapy, brachytherapy, radiotherapy or hormone therapy, which should be indicated by the oncologist according to the needs of each patient.
Consultation for periodic exams with a gynecologist and the control of risk factors such as diabetes and obesity is fundamental for this disease to be adequately treated.
Is Endometrial Cancer Cure?
Endometrial cancer is curable when it is diagnosed early in the disease and is treated appropriately according to the staging phase, which takes into account the spread of cancer (metastasis) and organs involved.
In general, endometrial cancer is classified in grade 1, 2 and 3, grade 1 being the least aggressive and grade 3, the most aggressive, in which metastasis can be observed in the internal wall of the intestine, bladder, or other organs .