The purple spots are caused by leakage of blood into the skin due to a rupture of blood vessels, usually caused by fragility of blood vessels, strokes, change in platelets or the ability to clot blood.
Most of the time, these spots, which are known as purpura or bruises, appear and disappear spontaneously, without causing symptoms, or may present mild local pain. In addition to strokes, some of the main causes for the appearance of purple spots on the skin are:
1. Capillary fragility

Capillary fragility occurs when small blood vessels responsible for the circulation of the skin are fragile and rupture spontaneously, causing blood leakage under the skin, and the main causes are:
- Aging, which can cause a weakening in the structures that form and sustain the vessels, so it is very common in the elderly;
- Allergies, in which there is angioedema, ie, swelling of the vessels due to an allergic reaction and that may rupture, causing bleeding;
- Genetic predisposition, which is very common in women, especially in certain periods of the menstrual cycle, which may also be associated with hormonal changes in women;
- Purple by melancholy, in which there are purple spots on the skin due to situations of stress, anxiety and mainly sadness, for unknown reasons;
- Vitamin C deficiency, which causes weakness in the walls of blood vessels, which may rupture spontaneously.
In some cases, however, the cause of capillary fragility is not detected, so some people may have purple spots more easily than others, without this indicating a disease or a health problem.
How to treat: purplish and ecchymoses due to capillary fragility usually appear and disappear spontaneously, without nothing having to be done. However, it is possible to make them add up faster with the use of hematoma ointments such as Hirudoid, Thrombocid or Desonol, for example, which decrease inflammation and facilitate blood reabsorption, reducing stain time.
Natural Treatment : A homemade treatment option is to take orange juice or vitamin C supplement, as it helps replenish collagen and heal the vessel more quickly. In addition, making compresses with warm water at the affected site also helps a reabsorption of the blood more quickly through the body.
2. Diseases that alter blood clotting

Some diseases can interfere with blood clotting, either by reducing the number of platelets or changing their function, or by changing blood clotting factors, which facilitates blood leakage through the blood vessels and the formation of blemishes. Some of the main causes are:
- Infections with viruses, such as Dengue and Zika, or bacteria, which affect platelet survival due to changes in immunity;
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals such as iron, folic acid and vitamin B12;
- Autoimmune diseases, which affect the survival of platelets due to changes in the person's immunity, such as lupus, vasculitis, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic-uremic syndrome or hypothyroidism, for example;
- Liver diseases, which interfere with blood clotting;
- Bone marrow diseases, such as aplastic anemia, myelodysplasia or cancer, for example;
- Genetic diseases such as hemophilia or hereditary thrombocytopenia.
The stains caused by diseases are usually more severe than by the capillary fragility, and their intensity varies according to the cause.
How to treat : Treatment of coagulation changes depends on the cause of the bleeding. Depending on your doctor's advice, the use of immune-modifying medicines such as corticosteroids, treatment of infections, blood filtration, withdrawal of the spleen, or, in the latter case, the transfusion of platelets. Understand better what are the main causes and how to treat platelet reduction.
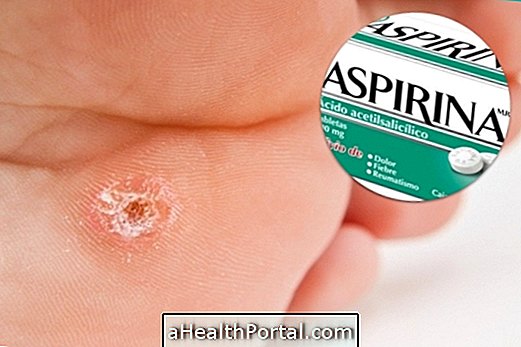
3. Use of medicines

Some medicines, such as aspirin, Clopidogrel, Paracetamol, Hydralazine, thiamine, chemotherapy or anticoagulant drugs, such as aspirin, are known to interfere with the blood's ability to coagulate or affect platelet action, such as purpura or ecchymosis. Heparin, Marevan or Rivaroxaban, for example.
How to treat : You should check with your doctor to remove or replace the medicine that causes bleeding and, during use, it is important to avoid strokes to reduce the risk of bleeding.
Causes of purple spots on infants
The purple spots that are already born with the baby, greyish or purplish in color, of various sizes or in various places of the body, are called Mongolian stains, and do not represent any health problem and are not the result of any trauma.
These spots disappear spontaneously around 2 years of age, without the need of any specific treatment, being guided about 15 minutes of sunbathing before 10am in the morning, per day. Learn how to identify and treat Mongolian spots.
Blotches that appear after birth may be the result of some local bump, capillary fragility, or, more rarely, of a coagulation disorder, and it is important to consult with the pediatrician to investigate the cause.
If these patches appear in large numbers, worsen throughout the day or are accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever, bleeding or drowsiness, contact your pediatrician or go to the pediatric emergency room immediately to assess the presence of diseases that interfere with coagulation, such as hereditary defects in blood coagulation, diseases that cause platelet changes, or infections, for example.