Red spots on the skin in adults may be related to diseases like Zika, rubella or a simple allergy. So, whenever this symptom appears, one should go to the doctor to identify their cause and initiate appropriate treatment, which may include the use of analgesics, anti-inflammatories or even antibiotics.
The doctor may see the spots and if there are other symptoms that may indicate some disease, he may also ask for tests that help to get to the diagnosis, but sometimes the doctor can arrive at the diagnosis of the disease only when observing the characteristics of the spots. Also know what may be blemishes on baby's skin.
Common causes of red spots on the skin
The main causes of red spots on the skin are diseases such as:
1. Allergy
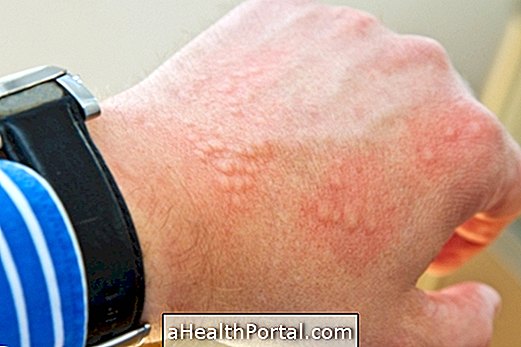
How are the spots: medium-sized, can be red or white, and itchy, can fill with liquid. They usually appear after contact with plants, animal hair or medicine intake, for example, but can also be caused by insect bites or food poisoning.
How to treat: Symptoms can be alleviated with allergy medicines, such as Loratadine, corticosteroids, such as Prednisone, or application of creams, such as Fenergan, prescribed by the dermatologist. See more about treatment.
Ringworm

As are the spots: they can be large and affect a well-delimited region of the body. In addition, there may also be blistering and flaking in the area. See details of mycosis symptoms on the skin.
How to treat: antifungal remedies and sometimes antibiotics can be indicated by the dermatologist.
3. Zika virus

As are the spots: gently raised reddish spots that are accompanied by itching, which usually appear 3 days after the mosquito bite. Zika stains usually appear first on the face and scatter the rest of the body in a few hours and last for about 5 days.
How to treat: Rest, hydration and remedies prescribed by the doctor to relieve symptoms and discomfort such as Dipirone or Paracetamol, for example. See How to know if you are with Zika.
4. Eczema

How are the spots: They cause a lot of itching and can become swollen. They are more common in children and health care professionals who wash their hands with antiseptic soaps. Learn how to identify Eczema.
How to treat: ingestion of anti-allergic medicines like Loratadine and application of ointments or corticoid creams, such as Fenirax, prescribed by the dermatologist.
5. Rubella

How are the spots: They are small, slightly raised and itchy. They usually start on the face and part behind the ears and soon spread through the body and last for about 3 days. Learn more about symptoms and treatment.
How to treat: Follow the doctor's advice that can be done with Paracetamol until the disease is properly controlled.
6. Psoriasis

As they are the spots: they present / display white center with red, dry edges, that descamam and that cause itch. They are most common before the age of 30 and after the age of 50, are not contagious and are related to genetic factors.
How to treat: application of dermatologist-oriented anti-inflammatory creams or ointments, sun exposure and changes in diet, such as avoiding fatty foods and processed products, and increasing the consumption of foods rich in omega-3 and beta-carotene. Learn about other important care during psoriasis treatment.
7. Lupus

As are the patches: reddish or flat spots that can appear on any part of the body, being more frequent in women. See other symptoms and how to treat.
How to treat: doctor-directed immunosuppressive and corticosteroid remedies.