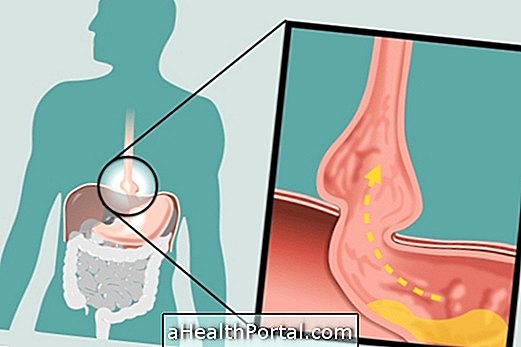
Diaphragmatic hernia arises when there is a defect in the diaphragm, which is the muscle that helps breathing, and which is responsible for separating the organs from the chest and abdomen. This defect causes the organs of the abdomen to pass into the chest, which may not cause symptoms or cause serious complications such as breathing difficulties, lung infections or digestive disorders, for example.
A diaphragmatic hernia can arise during the development of the baby in the mother's womb, leading to a congenital hernia, but can also be acquired throughout life, such as a chest trauma or complication of surgery or infection in the region. Understand how a hernia forms.
The identification of this problem is done through imaging tests such as X-ray or computed tomography. The treatment of diaphragmatic hernia is done by the general surgeon or pediatric surgeon, through surgery or video-surgery.
Main types
The diaphragmatic hernia can be:
1. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
It is a rare change, which arises from defects in the development of the baby's diaphragm even during pregnancy, and may arise in isolation from unexplained causes or be associated with other diseases, such as genetic syndromes.
The main types are:
- Bochdalek's hernia : is responsible for the vast majority of cases of diaphragmatic hernias, and usually appears in the region behind and the lateral diaphragm. Most are located on the left side, some appear on the right side, and a minority appears on both sides;
- Morgani hernia : result from a defect in the anterior region, in the front part of the diaphragm. Of these, most are located on the right;
- Esophageal hiatal hernia : arise due to excessive enlargement of the orifice through which the esophagus passes, which can result in the passage of the stomach into the thorax. Understand better how hiatus hernia arises, symptoms and treatment.
Depending on its severity, the formation of a hernia can cause serious consequences to the health of the newborn, since the abdominal organs can occupy the space of the lungs, caused alterations in the development of these, and also of other organs like intestine, stomach or heart, for example.
2. Acquired Diaphragmatic Hernia
It occurs when there is a rupture of the diaphragm due to a trauma to the abdomen, such as after an accident or perforation by weapon, for example, due to a thorax surgery or even an infection in the place.
In this type of hernia, any site of the diaphragm can be affected, and just like in the congenital hernia, this rupture in the diaphragm can cause the contents of the abdomen to pass to the chest, especially the stomach and intestines.
This can result in damage to the blood circulation to these organs, and in these cases can cause serious health risks to the affected person if not corrected quickly with surgery.
How to identify
In case of hernias that are not severe, there may be no symptoms, so it may remain many years until it is discovered. In other cases, there may be signs and symptoms such as breathing difficulties, intestinal changes, reflux, heartburn and poor digestion.
The diagnosis of diaphragmatic hernia is performed by imaging the abdomen and chest, such as x-ray, ultrasound or computed tomography, which can demonstrate the presence of undue content within the thorax.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment of the diaphragmatic hernia is the surgery, able to reintroduce the contents of the abdomen to its normal location, besides the correction of the defect in the diaphragm.
The surgical procedure can be performed with the aid of cameras and instruments indroduced by small holes in the abdomen, which is labaroscopic surgery, or by the conventional form, if it is a serious hernia. Know when laparoscopic surgery is indicated and how it is done.













-o-que--causas-e-tratamento.jpg)




