Patau's syndrome is a rare genetic disease that causes malformations in the nervous system, heart defects and cleft in the lip and the sky of the baby's mouth, and can be discovered during pregnancy through diagnostic tests such as amniocentesis and ultrasound.
Normally, babies with this disease survive less than 3 days on average, but there are cases of survival up to 10 years of age, depending on the severity of the syndrome.
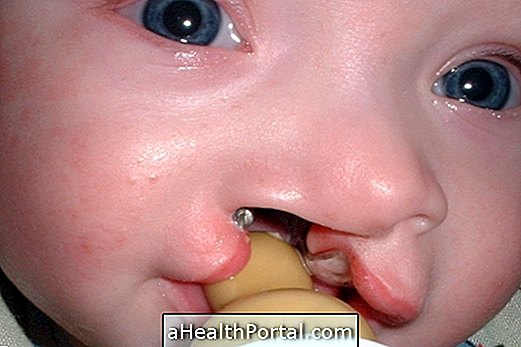
Characteristics of Patau Syndrome
The most common characteristics of children with Patau Syndrome are:
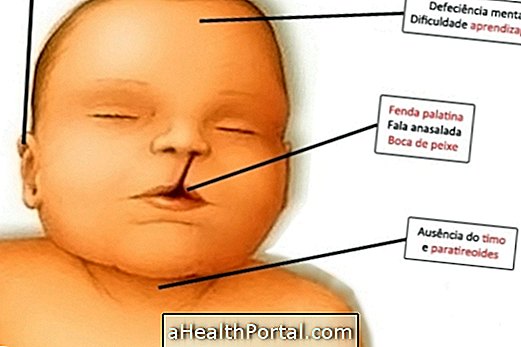
- Serious malformations in the central nervous system;
- Severe mental retardation;
- Congenital heart defects;
- In the case of boys, the testicles may not descend from the abdominal cavity to the scrotum;
- In the case of girls, changes in the uterus and ovaries may occur;
- Polycystic kidneys;
- Lip cleft and the roof of the mouth;
- Malformation of the hands;
- Defects in eye formation or absence of eyes.
In addition, some babies may also have low birth weight and a sixth finger on their hands or feet. This syndrome affects in greater number the babies with mothers who became pregnant after the 35 years of age.

How is the treatment done?
There is no specific treatment for Patau's syndrome. As this syndrome causes such serious health problems, the treatment is to relieve the discomfort and facilitate the baby's feeding, and if it survives, the following care is based on the symptoms that manifest themselves.
Surgery may also be used to repair heart defects or slits in the lips and upper lip, and to make physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy sessions that may assist in the development of surviving children.
Possible causes
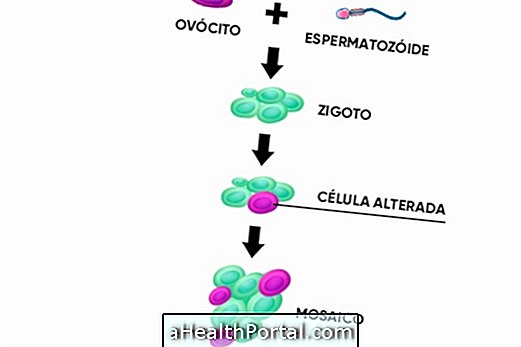
Patau syndrome occurs when an error occurs during cell division that results in a triplication of chromosome 13, which affects the development of the baby still in the mother's belly.
This error in the division of chromosomes may be associated with the advanced age of the mother, since the probability of trisomies occur is much higher in women who become pregnant after 35 years of age.