Lymphogranuloma venereum, also called mule, is a sexually transmitted disease caused by three different strains of the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, with the formation of painless, fluid-filled wounds in the intimate region that are not always perceived.
This disease is transmitted sexually, so it is important to use the condom in all intimate contacts, as well as pay attention to the hygiene of the intimate region after intercourse. Treatment is usually done with the use of antibiotics, which should be recommended by the doctor according to the sensitivity profile of the microorganism and symptoms presented by the patient.

Symptoms of venereal lymphogranuloma
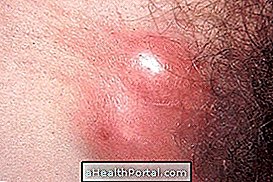
The symptoms of venereal lymphogranuloma appear between 3 and 30 days after infection and the main symptom is the presence of fluid-filled and painless wounds in the intima and usually disappear alone after 3 to 5 days. However, they appear again with an inflamed appearance, with pus and blood. Other symptoms of venereal lymphogranuloma are:
- Fever;
- Malaise;
- Vomiting;
- Headache in the back and in the joints,
- Lack of appetite;
- Weight loss;
- Night sweats;
- Inflammation in the rectum;
- Painful swelling in the groin.
If symptoms are not identified and the disease is treated quickly or in the right way, some complications can arise, such as penile and scrotal lymphedema, intestinal hyperplasia, vulvar hypertrophy and proctitis, which is the inflammation of the mucosa that lines the rectum and can happen if the bacteria were acquired through anal sex. Learn more about proctitis and how the treatment is done.
Lymphogranuloma venereum can be acquired through intimate contact without a condom, and is therefore considered a sexually transmitted disease. The diagnosis is made by analyzing the symptoms and blood tests that identify the antibodies against Chlamydia trachomatis, as well as the culture of wound secretion, which may be useful to identify the microorganism and to check the best antibiotic to be used as treatment .
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for venereal lymphogranuloma should be done according to medical advice, and antibiotics are usually recommended. The main drugs listed by doctors are:
- Doxycycline for 14 to 21 days;
- Erythromycin for 21 days;
- Sulfamethoxazole / trimethoprim for 21 days;
- Azithromycin for 7 days.
The antibiotic and the time of treatment should be indicated by the physician according to the sensitivity profile of the microorganism and the symptoms presented. Also, it is important for the person to have regular checkups to make sure that the treatment is actually taking effect, as well as their partner, who should be examined and treated even if they do not show symptoms.