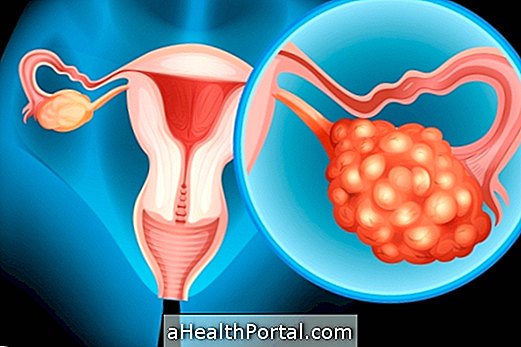
The Bartholin gland is located in the anterior part of the vagina and has the function of lubricating it, especially during intimate contact. However, this gland can ignite and become clogged due to the accumulation of fluid inside the gland itself, giving rise to Bartholin's cyst.
Bartholin's cyst is usually painless, has no symptoms and may have a spontaneous cure. However, when the fluid becomes infected with pus, giving rise to the infection of the gland, which is called acute Bartolinitis, the region may become reddish, swollen and very sore, and there may be pus.
In these cases, treatment is necessary and can be done with analgesic remedies, anti-inflammatory and antibiotics prescribed by the gynecologist, home remedies, hot water baths or surgery.
See what other types of cysts may appear in the vagina.

How to treat
Treatment of the inflamed Bartholin gland should be guided by the gynecologist, but is usually done with anti-inflammatory and analgesic remedies and, when there is infection, with antibiotics and hot water seat baths to relieve inflammation and eliminate pus.
Surgery for the Bartholin gland is indicated only when the Bartholin's cyst is formed and can be done by draining the cyst fluid, removing the cyst or removing Bartholin's own glands.
Learn more about treatment and see an excellent home treatment for inflamed Bartholin's gland.
Possible causes
The Bartholin gland can ignite and Bartholin's cyst formation may occur when the lubricating liquid builds up inside the gland itself. Already when infection of the bartholin cyst by bacteria, called bartolinite occurs, the causes can be:
- Practice of unprotected intimate relationships : Sexually transmitted bacteria, such as Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which causes gonorrhea, or Chlamydia trachomatis, responsible for chlamydia can reach the cyst, infecting it;
- Bad intimate hygiene care such as carelessness or improper washing of the region, back to front: bacteria in the intestinal tract, often Escherichia coli can infect the Bartholin gland.
In this way, the appearance of the Bartholin's cyst can be avoided through the use of condoms and the maintenance of adequate intimate hygiene habits.
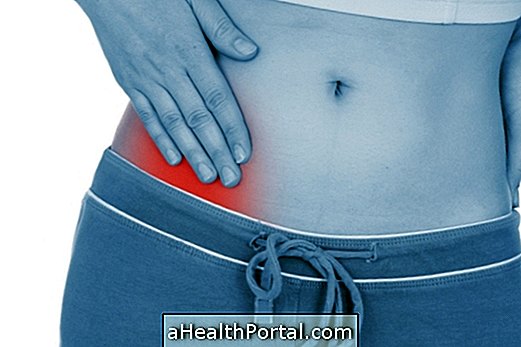
Main symptoms
Bartholin's cyst usually does not cause symptoms nor is it contagious, however, the woman may have the sensation of having a ball or lump in the vagina when it touches the region, and it may be swollen and red. When the cyst becomes infected, other symptoms such as:
- Exit of pus;
- Region reddish, hot, very sore and swollen, similar to a boil;
- Nodule near the vaginal opening, usually in the most advanced cases;
- Pain and discomfort while walking or sitting and during intimate contact;
- Fever.
In the presence of these symptoms, the gynecologist should be consulted to guide the treatment.
Inflammation of the Bartholin's gland in pregnancy
The inflammation of the Bartholin gland in pregnancy is usually not worrisome, because the appearance of the cyst is painless and eventually disappears naturally and, therefore, the woman may have normal birth.
When Bartholin's cyst becomes infected during pregnancy, with proper treatment, it is usually free of bacteria and there is no risk to the pregnant woman or baby.