Oximetry is the test capable of measuring the oxygen saturation of the blood, which is the percentage of oxygen being transported in the bloodstream. This measure is usually necessary when diseases that impair or interfere with the functioning of the lungs, such as asthma, emphysema, pneumonia, lung cancer or pulmonary congestion or neurological diseases are suspected, for example.
Generally, oximetry above 90% indicates good oxygenation of the blood, however, it is necessary for the physician to evaluate each case. A low blood oxygenation rate may indicate the need for treatments such as catheter or oxygen masks, and may indicate a life-threatening condition if proper treatment is not given. Understand the consequences of lack of oxygen in the blood.
The main ways to carry out this measure include:
1. Finger or pulse oximeter (Noninvasive measurement)


It is the way to measure the amount of oxygen in the blood with the use of small devices, called pulse oximeters, that can do this measurement only with the contact with the wrist when placed on a finger or in the wolf of the ear.
The main advantage of this measure is that it is not invasive, as it is not necessary to prick or collect blood from the patient. In addition to oximetry, this device may also be able to measure other vital data such as heart rate and respiratory rate.
- How it works : It has a light sensor that captures the amount of oxygen in the blood in the arteries and the frequency of heart beats only on contact with the skin. These sensors take immediate and regular measurements, and are designed for use on the fingers, toes, or the ear.
Pulse oximetry is widely used by physicians and other health professionals during clinical evaluation, especially in cases of diseases that cause difficulty in breathing, such as pulmonary, cardiac and neurological diseases, or during anesthesia.
The oximeter can be purchased at medical or hospital supply stores, and is available in different brands and prices. It is recommended to obtain reliable marks to avoid measurement errors.
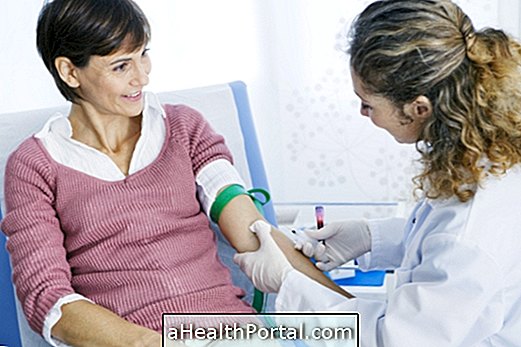
2. Arterial blood gas (Invasive measurement)


Arterial blood gas analysis is an invasive way of measuring the rate of oxygen in the blood, as it is done by collecting blood into a syringe, requiring a needle stick to access the blood vessel that carries arterial blood.
The advantage of arterial blood gases is a more accurate measure of blood oxygen saturation levels, as well as other important measures such as the amount of carbon dioxide, pH, or the amount of acids and bicarbonate in the blood, for example.
- How it works : For arterial blood gases it is necessary to collect blood for a syringe, and then this sample is taken to be measured in a specific device for this. The most commonly used blood vessels for this type of measurement are the radial or femoral artery, but others may also be used.
This type of measurement is usually used in cases where the patient needs to be monitored continuously or more accurately, which is more common in situations such as major surgery, severe heart disease, arrhythmias, generalized infection, sudden changes in blood pressure or in cases of respiratory failure, for example. Know what is respiratory failure and how it can decrease oxygenation of the blood.
Normal Values
A healthy person, with proper oxygenation of the body, usually has an oxygen saturation of over 95%. When saturation reaches values less than 90% may indicate that blood oxygenation is deficient, which can occur in diseases such as asthma, pneumonia, emphysema, heart failure or neurological diseases, for example.
In arterial blood gases, in addition to oxygen saturation, the partial pressure of oxygen (Po2), which must be between 80 and 100 mmHg, is also evaluated.
However, there is always a need for evaluation of the physician or health care provider, as other clinical data need to be evaluated to determine the cause and how the treatment should be done.
Oximetry Care
It is very important that the devices that make this type of measurement be calibrated regularly, to avoid altered results. In addition, during the use of the pulse oximeter, some precautions to avoid altering the exam include:
- Avoid using enamel or false nails as they change the passage of the light sensor;
- Protect the device in a bright or sunny environment;
- Check that the appliance is in the correct position;
In addition, the doctor should investigate diseases such as anemia or deficiencies in blood circulation, which can interfere with the extent of oxygenation of the blood.