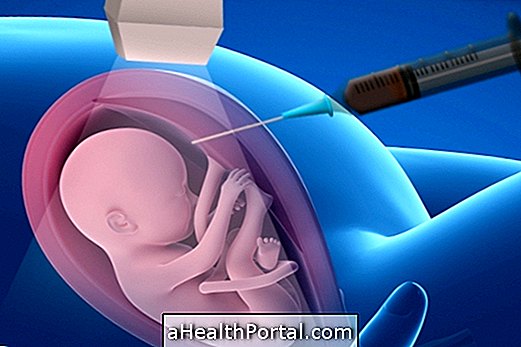
Cordocentesis, or fetal blood sample, is a prenatal diagnostic test, done at 18 or 20 weeks of gestation, in which a baby's blood sample is withdrawn from the umbilical cord to detect any chromosomal deficiency in the baby, such as Down Syndrome, or diseases such as toxoplasmosis, rubella, fetal anemia or cytomegalovirus, for example.
The main difference between cordocentesis and amniocentesis, which are two prenatal diagnosis tests, is that the cordocentesis analyzes the baby's umbilical cord blood, while the amniocentesis analyzes only the amniotic fluid. The karyotype results in 2 or 3 days, which is one of the advantages over amniocentesis, which takes about 15 days.
When to do cordocentesis
Indications of cordocentesis include the diagnosis of Down Syndrome, when it can not be obtained through amniocentesis, when the ultrasound results are inconclusive.
Cordocentesis allows the study of DNA, karyotype and diseases such as:
- Blood diseases: Thalassemia and sickle cell anemia;
- Blood clotting disorders: Hemophilia, Von Willebrand's disease, Aloimune thrombocytopenia, Thrombocytopenic purpura;
- Metabolic diseases such as Muscular Dystrophy of Duchene or Tay-Sachs Disease;
- To identify why the baby has a growth restriction, and
- To identify fetal hydrops, for example.
In addition, it is also very useful for the diagnosis that the baby has some congenital infection and may also be indicated as a form of treatment for intrauterine blood transfusion or when it is necessary to administer medicines in the treatment of fetal diseases, for example.
Learn about other tests for the diagnosis of Down Syndrome.
How is cordocentesis made?
No preparation is necessary before the examination, however, the woman must have done before ultrasound and a blood test to indicate her blood type and RH factor. This examination can be done in the clinic or hospital, as follows:
- The pregnant woman lies on her belly;
- The doctor applies local anesthesia;
- With the aid of ultrasound, the doctor inserts a needle more specifically in the place where the umbilical cord and the placenta are united;
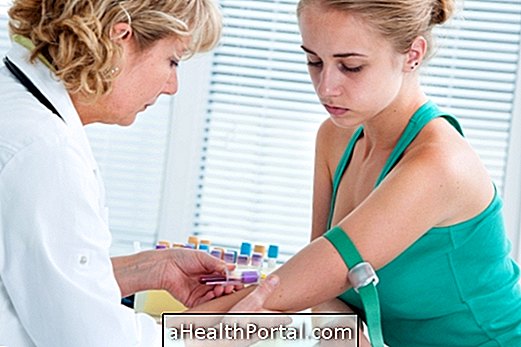
- The doctor takes a small sample of the baby's blood with about 2 to 5 ml;
- The sample is taken to the laboratory for analysis.
During the examination the mother may experience abdominal cramps and she should rest for 24 to 48 hours after the examination and not have intimate contact for 7 days after the cordocentesis.
Symptoms such as fluid loss, vaginal bleeding, contractions, fever and pain in the foot of the belly may occur after the examination. For relief of pain and discomfort it may be helpful to take one Buscopan tablet under medical indication.
What are the risks of cordocentesis?
Cordocentesis is a safe but risky procedure, just like any other invasive exam, so your doctor will ask you when there are more advantages than risks to the mother or baby. The risks of cordocentesis are low and contrived, but include:
- About 1 of abortion risk;
- Loss of blood where the needle is inserted;
- Decreased baby's heart rate;
- Premature rupture of the membranes, which may favor premature labor.
The doctor usually asks for cordocentesis when there is suspicion of any genetic syndrome or disease that has not been identified through amniocentesis or ultrasound.








-o-que--e-para-que-serve.jpg)




-causas-e-como-tratar.jpg)