The excess blood sugar, scientifically called hyperglycemia, occurs when the fasting blood glucose is above 100 mg / dL, a situation that if it is persistent can have bad consequences on the functioning of the organs so it must be treated properly with diet, physical exercises and physician-directed medications.
Although it generally does not cause symptoms, because it installs silently, when too much blood sugar is persistent or too high can cause:
- Thirst;
- Increased urge to urinate;
- Very hungry;
- Unexplained weight loss;
- Tiredness;
- Headache;
- Nipple;
- Somnolence;
- Tingling in the hands or feet;
- Blurry vision.
These symptoms are caused both by reactions due to too much sugar in the blood and by the lack of insulin to bring the glucose into the cells, leaving them without energy, most common situations when there is already diabetes installed. Thus, whenever glucose reaches persistent values above 126 mg / dL fasting, or 200 mg / dL at any time of the day, diabetes is diagnosed, a very dangerous disease that causes deficiency in the action of insulin and excess glucose in the blood .
Therefore, whenever these symptoms appear, it is important to consult with the general practitioner as soon as possible for the clinical evaluation and the initial tests that identify the blood glucose levels, as well as blood pressure, cholesterol levels and triglycerides, for example, situations that are also risks to cardiovascular health.
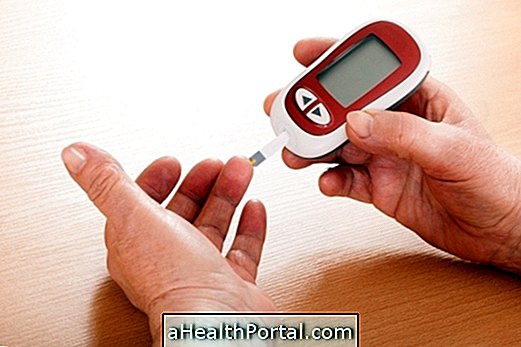
How to confirm
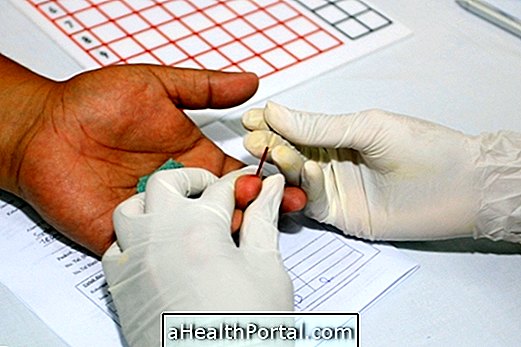
To diagnose excess blood glucose, the main test indicated is fasting glucose, which is already considered high when above 100 mg / dl or indicates diabetes when it is above 126 mg / dL.
Other tests also available for this function are the oral glucose tolerance test, postprandial glycemia, capillary glycemia or glycated hemoglobin, which should be requested by the doctor. Understand more about these tests that can confirm diabetes.
How to Lower Your Blood Sugar Level
In the case of an isolated hyperglycemia or when there is pre-diabetes, it is not necessary to use medicines, but it is very important to take care of food, avoiding excess sugar or carbohydrates, and investing in vegetables and whole foods, to avoid becomes diabetes. Check out how to identify and treat pre-diabetes.
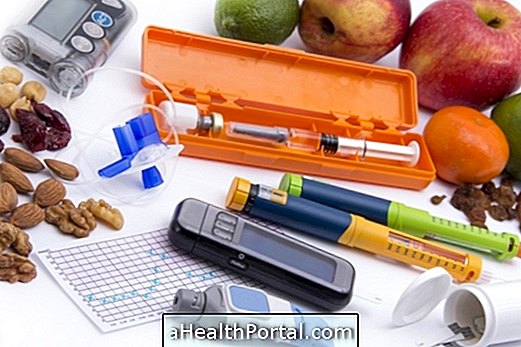
In the case of diagnosed diabetes, or in situations of excessive glycemia, it is necessary to use antidiabetic medicines, such as Metformin, Glibenclamide, Glimepiride, Gliclazide or even Insulin, for example. Diabetics should also be very careful about diet to avoid blood glucose spikes, as well as exercise and regular follow-up with bi-annual or annual medical appointments.
Some tips to keep your blood sugar from getting out of control are:
- Eat at regular intervals of 3 hours small meals;
- Do not eat concentrated sweets or isolated fruits as a meal;
- Do some physical activity like walking after the main meals and do not go to sleep or lie down.
A consultation with a nutritionist may also be helpful in clarifying important issues such as what to eat, when to eat, as well as foods you can not eat in the event of diabetes or pre-diabetes.