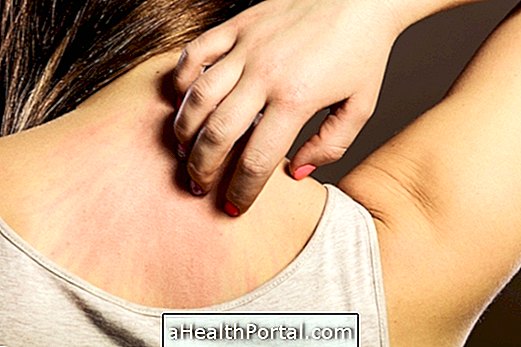
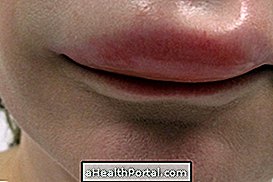
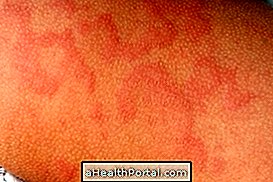
Urticaria is an allergic reaction in the skin that manifests itself through red spots that scratch and that usually become more swollen, as the image shows.
Usually, the symptoms of urticaria last up to 24 hours, disappearing without leaving marks or scars. However, blemishes can recur in other parts of the body, and when this happens for more than 6 weeks, urticaria is classified as chronic.

Urticaria can be controlled with the use of some medications, such as anti-allergy, and avoiding the causative factor of allergy whenever it is possible to identify it.
Symptoms of urticaria
The main symptoms of urticaria include:
- Reddish spots that become swollen;
- Scratchy spots with well-defined edges;
- Swelling of the lips, eyes, throat.
These symptoms may be located in a particular region or scattered throughout the body depending on what originated it.
It is recommended to go to the hospital whenever the symptoms of urticaria last more than 48 hours, difficulty swallowing and breathing or when you feel the throat swelling.
Treatment for urticaria
The treatment of urticaria should be started with the solution of your cause and can be resolved after washing the affected area with soap and water to eliminate an allergic substance, for example.
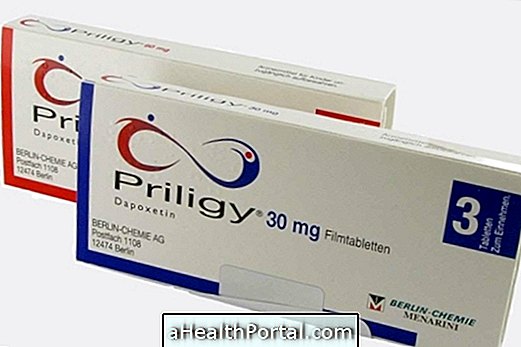
However, in cases where it is not possible to identify the cause of urticaria, your doctor may prescribe antiallergic medicines such as Loratadine, Cetirizine and Hydroxyzine, or oral steroids, such as Prednisone, to relieve itching and swelling.
In addition, it is possible to use cold compresses or soothing creams with menthol or camphor, for example, to decrease the symptoms of urticaria.
Learn more about how this problem is treated according to the type of urticaria.
Main causes of urticaria
The causes of urticaria can be varied, but the most common include:
- Bee sting;
- Allergic to clothing fabric, pollen, latex, sweat, for example;
- Dyes or food preservatives;
- Excessive stress;
- Extreme heat or cold;
- Food, such as peanuts, eggs, seafood;
- Infections, such as mononucleosis;
- Cleaning products, toxic products or toxic plants;
- Diseases such as lupus or leukemia.
It is not always possible to find out the cause of urticaria, however, the allergist doctor may do blood tests and allergy tests to try to better understand the symptoms and adjust the treatment.
Types of urticaria
The main types of urticaria are acute urticaria and chronic urticaria, depending on how long the allergy lasts.
However, urticaria can be divided according to its cause, such as:
- Emotional or nervous urticaria : it is related to emotional factors like excess of stress or anxiety and, therefore, the symptoms are more intense during phases of greater tension. Learn more about this type of hives;
- Cholinergic urticaria: it arises after an increase in body temperature, due to hot baths, hot foods or physical exercise, for example, and the symptoms last for about 90 minutes;
- Urticaria pigmentosa: caused by excess cells of the immune system, known as mast cells, in the skin, being more common in infants and children;
- Contact urticaria: arises after contact with allergenic substances, such as latex or resin, for example;
- Solar urticaria: caused by exposure to the sun and, therefore, the patient should avoid being exposed to the sun's rays.
In addition to these, there is still vasculitis, which is a rarer type of urticaria that causes inflammation of the veins, which can cause symptoms such as pain or burning in the affected area.