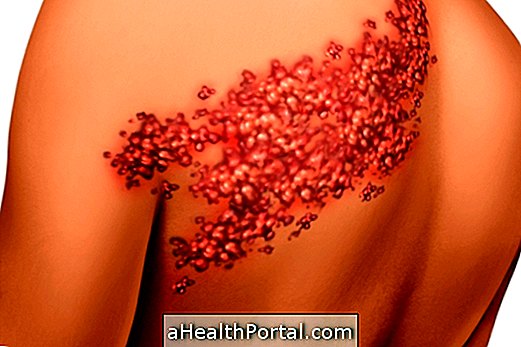
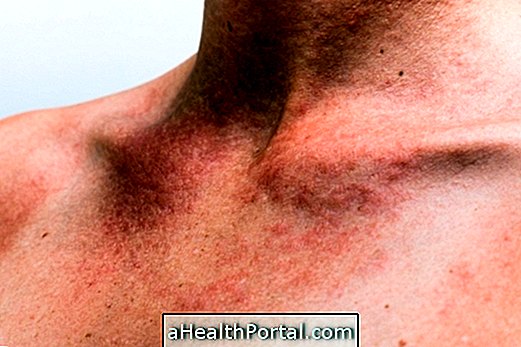
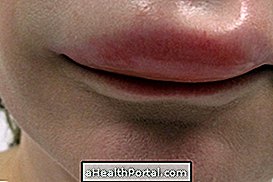
Angioedema is a disease that causes swellings to appear on the deeper layer of the skin, especially on the lips, hands, feet, eyes or genital area, which can last up to 3 days.
Depending on the cause of angioedema there are 3 major types which include:
- Hereditary angioedema: arises from birth and can pass from parents to children due to changes in genes. Learn how to identify and treat Hereditary Angioedema;
- Allergic angioedema: caused after contact with allergic substances such as peanuts or dust, for example;
- Idiopathic angioedema: There is no specific cause for angioedema, but it may arise in situations of stress or infection, for example;
- Drug- induced angioedema: Caused by the side effects of high blood pressure medicines such as Amlodipine and Losartan.
Angioedema is cured when it is caused by an allergic reaction or by ingestion of medicines, however, in other cases, it can not be cured and, therefore, situations that cause its onset should be avoided.
Photos of angioedema

How to treat angioedema
The treatment for angioedema should be guided by a dermatologist and usually varies according to the type of angioedema, and in cases of allergic, idiopathic or drug-induced angioedema, it is done with the ingestion of antihistamines such as Cetirizine or Fexofenadine, and steroid medicines such as Prednisone, for example.
The treatment of hereditary angioedema should be done with medicines that prevent the development of angioedema over time, such as Danazol, tranexamic acid or Icatibant. In addition, it is recommended to avoid situations that may lead to angioedema.
Symptoms of angioedema
The main symptom of angioedema is swelling of the skin at various body sites that lasts up to 3 days and does not cause itching, however other symptoms include:
- Sensation of heat in the affected region;
- Pain in the sites of swelling;
- Difficulty breathing.
In more severe cases, angioedema may still cause swelling of the intestine or throat, causing cramps, diarrhea, or difficulty breathing.
In addition, if angioedema is not treated properly, symptoms of anaphylactic shock, such as sweating or itching, may develop. See other symptoms in: Symptoms of anaphylactic shock.
When to go to the doctor
It is advisable to go to the ER immediately when:
- Feeling tight in the chest;
- Very difficult to breathe;
- Swelling of the tongue or throat.
In these cases, if the patient has an adrenaline injection for anaphylactic shock prescribed by the doctor, he should inject it while waiting for medical help.