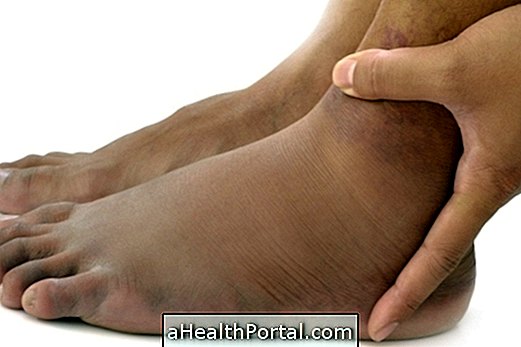
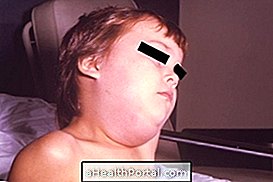
Angioedema is a condition characterized by deeper swelling of the skin, mainly affecting the lips, hands, feet, eyes or genital region, which can last up to 3 days and be quite uncomfortable. In addition to the swelling, there may also be a feeling of heat and burning in the area and pain in the swelling area.
Angioedema is curable when it is caused by an allergic reaction or ingestion of medications, in which case it is only recommended that the person avoid contact with the substance responsible for the allergy or suspend the use of the medication according to the doctor's guidance. In some cases, the doctor may also recommend the use of antihistamines or corticosteroids to relieve the symptoms associated with angioedema.

Main symptoms
The main symptom of angioedema is swelling of the skin in various parts of the body that lasts up to 3 days and does not cause itching. However, other symptoms may appear, such as:
- Sensation of heat in the affected region;
- Pain in the swelling sites;
- Difficulty breathing due to swelling in the throat;
- Swelling of the tongue;
- Swelling in the intestine, which can result in cramps, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
In some cases the person may still experience itching, excessive sweating, mental confusion, an increase in heart rate and feeling faint, which may be indicative of anaphylactic shock, which should be treated immediately to avoid complications. Learn more about anaphylactic shock and what to do.
Why it happens
Angioedema happens as a consequence of an inflammatory response of the body to an infectious or irritating agent. Thus, according to the related cause, angioedema can be classified into:
- Hereditary angioedema: it arises from birth and can pass from parents to children due to changes in genes.
- Allergic angioedema: caused after contact with allergic substances, such as peanuts or dust, for example;
- Remedy angioedema: caused by the side effects of medicines for high blood pressure, such as Amlodipine and Losartan.
In addition to these, there is also idiopathic angioedema, which does not have a specific cause but which usually arises as a result of situations of stress or infections, for example.
How the treatment is done
Treatment for angioedema should be guided by an allergist or dermatologist and usually varies according to the type of angioedema, and in cases of allergic, idiopathic or drug-induced angioedema it is done with the ingestion of antihistamines, such as Cetirizine or Fexofenadine, and corticosteroid medications, such as Prednisone, for example.
The treatment of hereditary angioedema should be done with drugs that prevent the development of angioedema over time, such as Danazol, Tranexamic acid or Icatibanto. In addition, it is recommended to avoid situations that may cause angioedema.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther