The first symptoms when being infected with the AIDS virus include general malaise, fever, dry cough and sore throat, often resembling the symptoms of a common cold, these last for approximately 14 days, and may appear 3 to 6 weeks after contamination with HIV.
Contamination usually occurs through risky behavior, where there was intimate contact without a condom or exchange of needles, for example. The test to detect the virus should be done 40 to 60 days after the risk behavior, because before that period the test may not detect the presence of the virus in the blood.
To learn more about this disease, watch the video:

Main symptoms of AIDS
The main symptoms of AIDS are manifested only if the person does not take any treatment against the virus, arising about 8 to 10 years after HIV infection or in certain situations where the immune system is weak and weak. Thus, the symptoms can be:
- Persistent fever;
- Prolonged dry cough and scratchy throat;
- Night sweats;
- Swollen lymph glands for more than 3 months;
- Headache and difficulty concentrating;
- Pain in muscles and joints;
- Tiredness, fatigue and loss of energy;
- Fast weight loss;
- Oral or genital candidiasis that does not go away;
- Diarrhea for more than 1 month, nausea and vomiting;
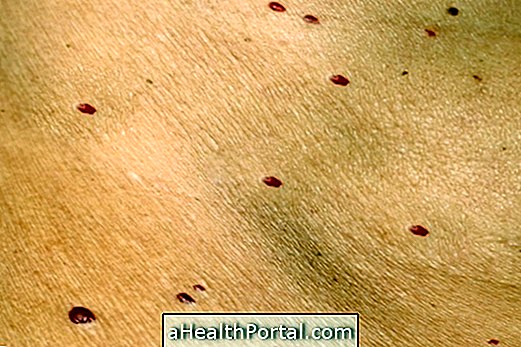
- Reddish spots and small red spots or sores on the skin.
These symptoms usually arise when the HIV virus is present in large quantities in the body and the defense cells have very low numbers compared to a healthy adult individual. In addition, at this stage where the disease has symptoms, opportunistic diseases usually develop, such as viral hepatitis, tuberculosis, pneumonia or toxoplasmosis, for example, because the immune system is weak and weak.
But about 2 weeks after coming in contact with the HIV virus the person may have symptoms that go undetected, such as low fever and malaise. See a complete list of these early symptoms of AIDS.

How do I know if I can be HIV-positive?
To find out if you are infected with the HIV virus, you should identify whether or not you have had any risk behavior such as unhealthy relationships or share syringes, and be aware of symptoms such as fever, general malaise, sore throat and dry cough.
After 40 to 60 days of risky behavior, it is recommended to have a blood test to find out if you have HIV, then repeat the test after 3 and 6 months again because even if you do not show symptoms you may have been infected with the virus. In addition, if you still have questions about what to do in case of suspected AIDS or when to take the test, read What to do if you suspect AIDS.
How is the treatment of AIDS?
AIDS is a disease that has no cure and therefore its treatment has to be done for a lifetime, and the main goal of treatment is to strengthen the immune system and fight the virus, controlling and reducing their amount in the blood.
Ideally, you should start HIV treatment before AIDS manifests itself. This treatment can be done with a cocktail with different remedies such as Efavirenz, Lamivudine and Viread that are provided free of charge by the government, as well as all the examinations needed to assess disease progression and viral load.