Kernicterus is a complication of neonatal jaundice that causes lesions in the newborn's brain when excess bilirubin is not treated properly.
Bilirubin is a substance that is produced by the natural destruction of red blood cells and their excess is eliminated by the liver in the production of bile. However, since many babies are born with a poorly developed liver, bilirubin eventually accumulates in the blood, resulting in neonatal jaundice that causes symptoms such as yellowing of the skin.
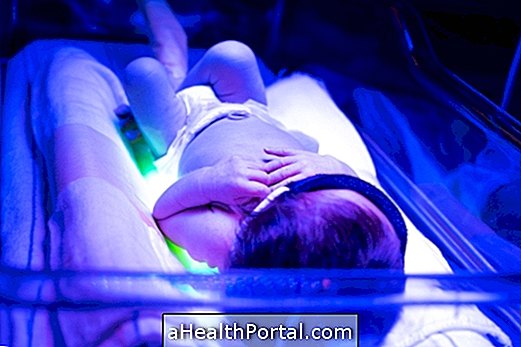
To prevent this substance from continuing to accumulate and prevent the development of kernicterus, your pediatrician recommends that you take the treatment with a special type of lights, as soon as the diagnosis of jaundice is confirmed, allowing the excess of bilirubin to be eliminated from the baby's body.
Main symptoms
Symptoms that may indicate that the baby is at higher risk of developing kernicterus are:
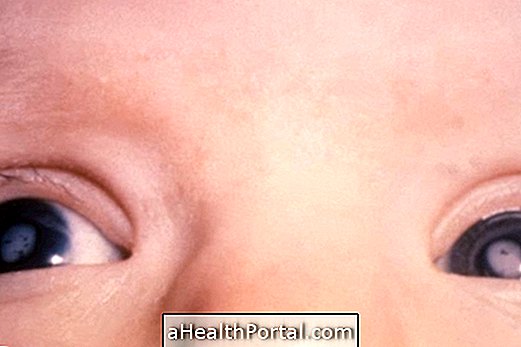
- Skin and yellow eyes;
- Difficulty in suckling;
- Very dark urine;
- Clear stools.
These symptoms do not indicate that the baby is with kernicterus, being only indication that it may be with neonatal jaundice, which is when there is excess bilirubin in the body. Kernicterus will only develop if treatment is not done and bilirubin continues to accumulate until it reaches the brain and causes lesions that can cause paralysis or deafness, for example.
How is the treatment done?
The best way to reduce bilirubin levels in the blood and prevent the kernicterus from arising or continuing to thrive is to put your baby on the road with special lights. This technique is known as phototherapy and allows bilirubin to be destroyed and eliminated more easily from the body.
However, when bilirubin levels are too high or the kernicterus is causing brain damage, the doctor may also advise making a blood transfusion to replace the baby's blood.
Possible sequels
When bilirubin levels get elevated for a long time in the blood, bilirubin can reach the brain, causing lesions that can generate sequelae such as:
- Cerebral palsy;
- Deafness;
- Vision problems;
- Difficulties of intellectual development.
These sequelae may vary according to the severity of the lesions and the affected brain areas.