Symptoms of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma usually include swollen glands, fever, weight loss, night sweats and easy tiredness. However, there may be other symptoms, depending on where the cancer is developing. These symptoms may also be known as B-symptoms and are more common in lymphomas that develop very quickly.
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is a type of solid tumor in the immune system responsible for the body's defenses that has a greater chance of cure when it is an aggressive tumor and rare metastases are rare, which increases the chances of cure of this type of cancer. Its treatment can be done with radiotherapy, chemotherapy and the use of monoclonal medicines, as indicated by the oncologist. Understand what this lymphoma is and how it is classified.

Main Symptoms of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Virtually all people who develop this type of cancer have:
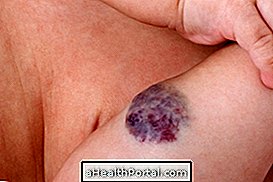
- Swollen and painful tongues, like small lumps in the neck, behind the ears, armpits, groin;
- Fever, fatigue easy and little energy to carry out the activities of the day to day;
- Loss of 10% of the weight in 6 months without diet or practice of physical exercises,
- Sur night to the point of waking up with wet clothes even during winter.
Other symptoms that may indicate non-Hodgkin's lymphoma located in certain regions of the body are:
| Lymphoma in the abdomen | Lymphoma in the chest | Lymphoma in the brain |
| Swollen and sensitive belly | Frequent cough | Headache |
| Feeling full of stomach after eating little food | Difficulty breathing | Difficulty thinking or talking |
| Abdominal pain | Chest pain or pressure feeling | Excessive weakness and tiredness |
| Nausea and vomiting | Swelling in the face or arms | Double Vision |
When non-Hodgkin's lymphoma affects the bone marrow can also hinder the production of healthy blood cells, leading to the emergence of serious and frequent infections or easy bleeding and bruising. In this case there may be anemia and decreased platelets.
However, in most cases initially lymphoma does not cause any type of symptom, only being identified in more advanced stages when it causes swelling of the anus or is identified in tests performed for any other reason. It is therefore recommended to go to the doctor whenever symptoms appear that do not disappear after a few days or weeks.
Confirmation of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
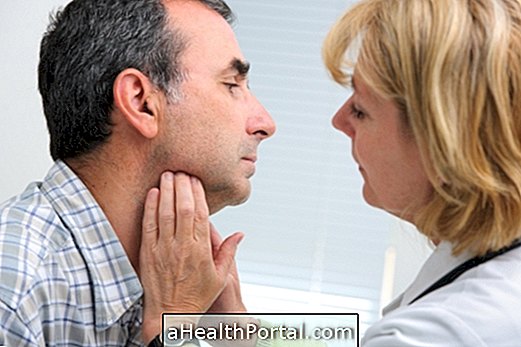
The diagnosis of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma can be made by observing the symptoms and assessing the patient's history, however, it is also necessary to perform tests such as:
- Complete blood count;
- X-ray;
- Computed tomography or MRI of the whole body and
- Biopsy;
- Lumbar puncture to check if cerebrospinal fluid has been affected and if there are signs of central nervous system involvement.
These tests serve to confirm the existence of the disease and to identify the type of tumor and its type and staging, which is essential for the choice of treatment. See how the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is done.
Some conditions that may favor the development of a lymphoma are autoimmune diseases such as Sjogren's Syndrome, celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, HIV infection 1, exposure to radiation or use of medications such as phenytoin or dioxin. However, it is not always possible to find out the cause of the development of this tumor.