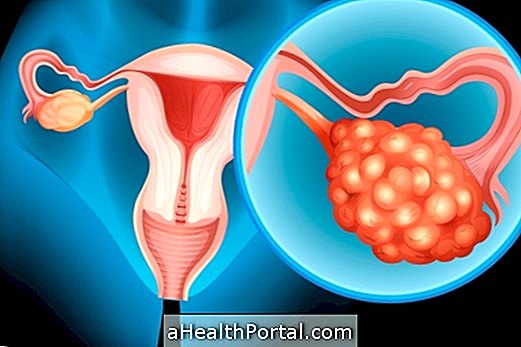
Hemorrhagic cyst occurs when a cyst on the ovary shows the breakage of a small vessel and bleeds into its interior. The ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled pouch that may appear in the ovary of some women, which is benign, and common in women between the ages of 15 and 35, and may be of various types, such as follicular cyst, corpus luteum, or endometrioma, for example. Learn about the types of ovarian cysts and the symptoms they cause.
The hemorrhagic cyst does not usually change fertility, but it can make pregnancy difficult if it is a type of cyst that produces hormones that alter ovulation, as in the case of the polycystic ovary, for example. It usually appears and disappears naturally throughout the menstrual cycles, and usually does not require treatment, except in more severe cases where surgery may be necessary.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic cyst
The symptoms of the hemorrhagic cyst in the ovary can be:
- Pain on the left side of the belly, when there is hemorrhagic cyst in the left ovary;
- Pain on the right side of the belly, when there is a hemorrhagic cyst on the right side;
- Colic;
- Pain during intimate contact;
- Delay of menstruation;
- Numbness;
- Vomiting;
- Slimming without apparent cause;
- Signs of anemia such as weakness, pallor, tiredness or dizziness;
- Breast tenderness.
These symptoms arise when the cyst becomes very large, due to the accumulation of blood inside it, causing pressure on the walls of the ovary, and are most evident during menstruation. Some types of cyst may produce hormones, such as progesterone, and in these cases, in addition to symptoms, there may be greater difficulty in getting pregnant.
In addition, when a hemorrhagic cyst ruptures, there may be burning sensation or severe belly pain, in which case an urgent consultation with a gynecologist is recommended.
How to identify
The presence of the hemorrhagic cyst is diagnosed with transvaginal or pelvic ultrasound, which will show its location, presence of bleeding and size, which, although rare, can reach up to 50 cm in diameter. Blood tests can help identify hormone produced and track the size of the cyst with request for semiannual or yearly ultrasound.

How is the treatment done?
Generally, the treatment of the hemorrhagic cyst consists of the use of analgesics, like dipirone, under medical guidance, since the cysts tend to disappear naturally at the end of 2 or 3 menstrual cycles. To aid in the relief of pain and inflammation, hot water bags, heating pads and ice packs can be applied in the pelvic region to stimulate blood circulation.
Oral contraceptives also help treat the hemorrhagic cyst in the ovary by decreasing the production of the hormones that stimulate cyst growth.
Laparoscopic surgery may be necessary in case of rupture of the hemorrhagic cyst with too much bleeding, to avoid further inflammation in the abdomen.
As a natural treatment, Quixaba tea is an excellent alternative to help in treatment as it has anti-inflammatory and healing properties. Learn the recipe of home remedy for ovarian cyst.
Can the hemorrhagic cyst become cancer?
The hemorrhagic cyst is usually benign, however, there are cases of ovarian cancer that can manifest as cysts. Thus, cysts in the ovary that have the highest risk of being cancer are those that have the characteristics:
- Presence of markers of cancer in the blood, such as CA-125;
- Cyst with solid components inside;
- Cyst greater than 5 cm;
- Presence of several cysts together;
- Extravasation of fluid out of the cyst;
- Presence of irregular borders and septa.
The treatment of cancer in the ovary consists of removing the committed ovary, through a surgery done by the gynecologist or general surgeon. See more on how to know if it is ovarian cancer and treatment.