Blenorrhagia is an STD caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, also known as gonorrhea, which is highly contagious, especially while the symptoms are manifesting.
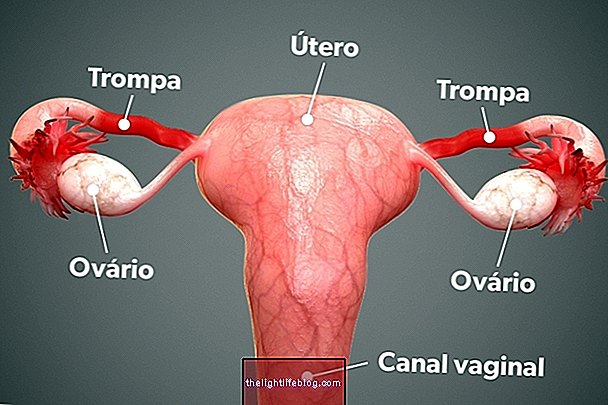
The bacteria responsible for the disease contaminates the individual by simply contacting the mucosa of the genitals, throat or eyes. Gout is an STD that causes inflammation of the genital mucous membranes of both men and women, although the symptoms in men have different characteristics from the symptoms in women. The disease evolves spread through the body through the bloodstream and can endanger the sex glands and even cause diseases in the bones and joints. So starting treatment as soon as possible is very important.
Symptoms of gonorrhea
Symptoms of gonorrhea in women:
- Yellowish discharge and burning when urinating.
- Urinary incontinence;
- There may be inflammation of the Bartholin glands;
- There may be sore throat and voice impairment (gonococcal pharyngitis, when there is an oral intima relationship);
- There may be obstruction of the anal canal (when there is anal intima relationship).
About 70% of women do not have symptoms.
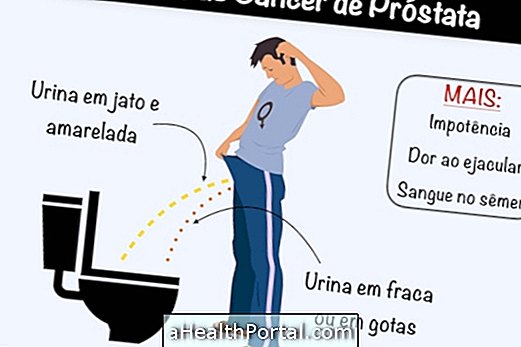
Symptoms of gonorrhea in man:
- Pain or burning when you urinate;
- Low fever;
- Yellow discharge, similar to pus, coming from the urethra;
- There may be sore throat and voice impairment (gonococcal pharyngitis, when there is an oral intima relationship);
- There may be obstruction of the anal canal (when there is anal intima relationship).
These symptoms may appear 3 to 30 days after unprotected intimate contact.
The diagnosis of gonorrhea can be made by observing the symptoms presented and confirmed through culture tests.
Treatment for gonorrhea
Treatment for gonorrhea should be performed with antibiotics such as azithromycin in a single dose or for approximately 10 consecutive days or at the discretion of the physician. Learn more about Gonorrhea Treatment.
The prevention of gonorrhea consists in the use of condoms in all relationships.