Fanconi Syndrome is a rare kidney disease and leads to the accumulation of glucose, bicarbonate, potassium, phosphates and certain excess amino acids in the urine. In this disease there is also loss of protein by the urine and the urine becomes stronger and more acidic.
Hereditary Fanconi Syndrome is caused by genetic changes that are passed from father to son. In the case of acquired Fanconi Syndrome, ingestion of heavy metals such as lead, ingestion of expired antibiotics, vitamin D deficiency, kidney transplantation, multiple myeloma or amyloidosis may lead to the development of the disease.
Fanconi Syndrome has no cure and its treatment consists mainly in the replacement of substances lost in the urine, as indicated by the nephrologist.
Symptoms of Fanconi Syndrome
The symptoms of Fanconi Syndrome can be:
- Urinate large amount of urine;
- Strong and acid urine;
- Very thirst;
- Dehydration;
- Short;
- Elevated blood acidity;
- Weakness;
- Pain in the bones;
- Coffee-colored skin blemishes with milk;
- Absence or defect in thumbs;
Generally, the characteristics of hereditary Fanconi Syndrome appear in childhood around the age of 5 years.
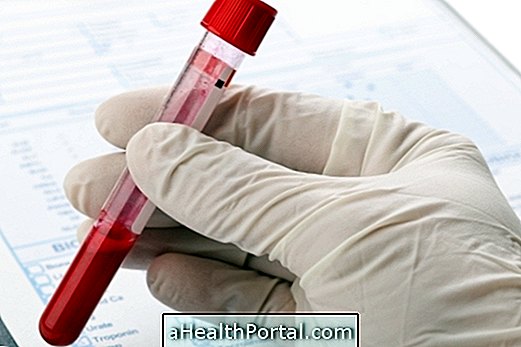
The diagnosis of Fanconi Syndrome is performed based on the symptoms, a blood test that reveals high acidity and a urine test that shows excess glucose, phosphate, bicarbonate, uric acid, potassium and sodium.
Treatment of Fanconi Syndrome
The treatment of Fanconi Syndrome aims to supplement the substances lost by individuals in the urine. For this, patients may need to take potassium, phosphate and vitamin D supplementation as well as sodium bicarbonate to neutralize blood acidosis.
In patients with severe renal impairment, kidney transplantation is indicated.
Useful links:
- Foods rich in potassium
- Foods rich in vitamin D
Kidney Transplantation