AIDS is a highly contagious viral infection that can be transmitted by blood, sperm, vaginal secretion, breast milk or blood transfusion from a carrier of the HIV virus.
Because the virus can be transmitted even before the carrier knows that it has the disease, it is important to avoid all risky contact, such as not using a condom and sharing syringes, to protect against AIDS.
The most common forms of AIDS contagion are:
- Intimate contact without condom with HIV-infected individual;
- Needles, syringes or perforating instruments contaminated with the HIV virus;
- Transmission of the HIV virus from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding.
On the other hand, one does not get AIDS through:
- Being close to a carrier of the AIDS virus, greet him with a hug or a kiss;
- Intimate relationship and condom masturbation;
- Use of the same dishes, cutlery or glasses;
- Harmless secretions like sweat and tears;
- Use the same hygiene material as soap, towel or sheets.


AIDS is also not transmitted through insect bites, through air or through pool or sea water.
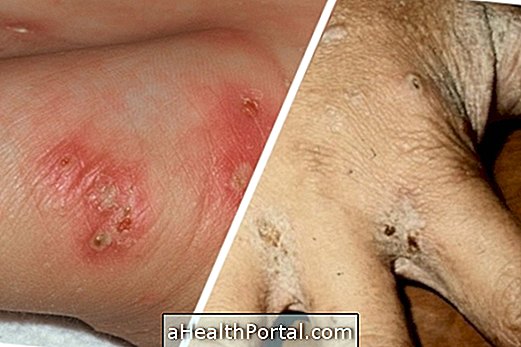
If you suspect that you have been infected, look at the symptoms of AIDS:

Learn more at: Symptoms of AIDS.
Where to take the HIV test
The HIV test can be done free of charge at any AIDS Testing and Counseling Center or health posts, spread across the country, anonymously.
To find out where to take the AIDS test and get other information about the disease and the results of the examination, you can call the Health Dial: 136 or Dial-Aids for free: (0xx21) 2518 2221.
The test can also be done at home properly and safely. See: HIV home testing.
Treatment of AIDS
AIDS treatment is done by ingestion of a cocktail of medicines. These should be taken daily and fight against HIV, strengthening the immune system. In addition, it is important to practice regular physical exercises; psychological and nutritional monitoring. Learn more at: AIDS Treatment.