Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease, which is usually silent because in 80% of cases it has no symptoms and is very common in young men and women up to 25 years of age.
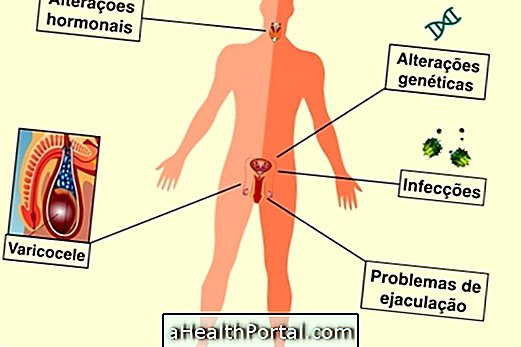
This disease is caused by a bacterium called Chlamydia trachomatis and when untreated can have serious consequences for both men and women with greater severity for women of reproductive age.
Women infected with chlamydia and who present such complications have a large risk of developing a pregnancy outside the uterus, called an ectopic pregnancy, which prevents the development of the baby and can cause maternal death.
Consequences of Chlamydia
The main consequences of infection by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis can be seen in the table below:
| Men's | Women |
| Non-Gonococcal Urethritis | Salpingitis: Chronic inflammation of fallopian tubes |
| Conjunctivitis | DIP: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease |
| Arthritis | Infertility |
| --- | Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy |
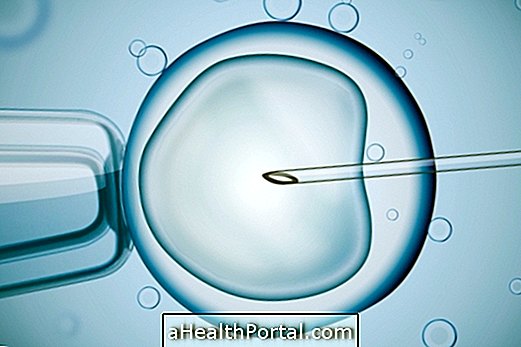
In addition to these complications, when infected women opt for in vitro fertilization because they can not conceive naturally, they may not succeed because chlamydia also decreases the success rates of this method. However, in vitro fertilization continues to be indicated for these cases because it may still have some success, but the couple should be aware that there will be no guarantee of pregnancy.
Why does chlamydia cause infertility?
The way this bacterium causes infertility is not yet fully understood, but it is known that the bacterium is transmitted sexually and that it reaches the reproductive organs and can cause serious alterations, such as salpingitis that inflames and deforms the uterine tubes.
Although the bacterium can be eliminated, the damages caused by it can not be cured and therefore the affected person becomes sterile because inflammation and deformation in the tubes prevents the egg from reaching the fallopian tubes, where the fertilization usually occurs .
How to know if I have Chlamydia
It is possible to identify chlamydia through a specific blood test where it is possible to observe the presence of antibodies against this bacterium. However, this test is not normally required only when the person has symptoms that may indicate Chlamydia infection such as pelvic pain, yellowing of the skin or pain during the intimate period or when there is suspicion of infertility that arises when the couple is trying to get pregnant more of 1 year, without success.
What to do to get pregnant
For those who have found that you have chlamydia before you observe infertility, it is recommended to follow the doctor's advice, taking the antibiotics correctly to decrease the risk of complications.
Chlamydia has a cure and the bacteria can be eliminated from the body after the use of antibiotics prescribed by the doctor, however, the complications caused by the disease are irreversible and so the couple may not be able to conceive naturally.
Thus, those found to be infertile due to the complications of chlamydia may choose assisted reproduction, using methods such as IVF - In Vitro Fertilization.
To avoid chlamydia it is recommended to use a condom in all sexual relations and go to the gynecologist or urologist at least once a year for the doctor to look at the person's genitals and ask for exams that may indicate a change. Also, it is important to go to the doctor whenever you experience symptoms such as pain during intimate contact or discharge.