The tubal obstruction can be treated with surgery to remove the damaged part or remove the tissue blocking the tube, thus allowing the passage of the ovum and natural pregnancy. This problem can occur in only one trunk or both, when it is called a bilateral obstruction, and usually causes no symptoms, so that the problem is only identified when the woman can not become pregnant.
However, when the obstruction can not be resolved through surgery, the woman may use other alternatives to conceive, such as:
- Treatment with hormones: used when only one horn is obstructed as it stimulates ovulation and increases the chances of pregnancy through the healthy horn;
- In vitro fertilization: used when the other treatments did not work, because the embryo is formed in the laboratory and then implanted in the womb of the woman. See more details on the In Vitro Fertilization procedure.
In addition to reducing the chances of getting pregnant, the obstruction in the tubes can also cause ectopic pregnancy, which when untreated can lead to rupture of the fallopian tubes and risk of death for the woman.


Diagnosis of tubal obstruction
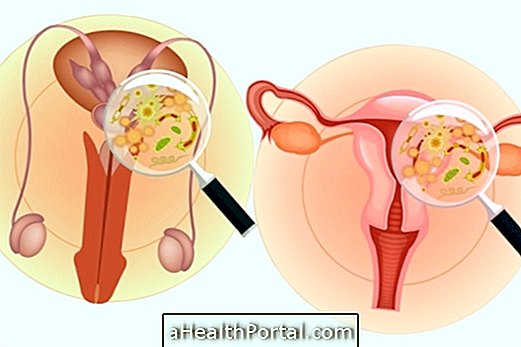
The diagnosis of tubal obstruction can be made through an examination called hysterosalpingography, in which the gynecologist can analyze the tubes through a device placed in the woman's vagina. See details on how the test is performed in: Hysterosalpingography.
Another way to diagnose tubal obstruction is through laparoscopy, which is a procedure where the doctor can see the tubes through a small cut that is done in the belly, identifying the presence of obstruction or other problems. Here's how this procedure is done: Videolaparoscopy.
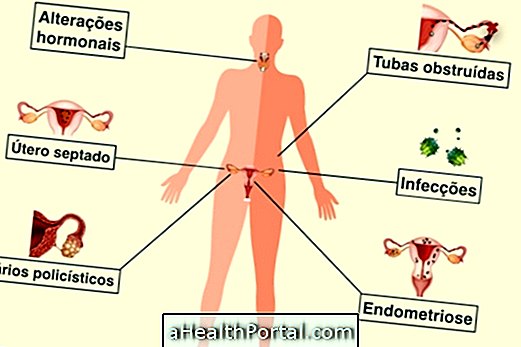
Causes of Tubal Obstruction
Tubal obstruction can be caused by:
- Abortion, especially without medical care;
- Endometriosis;
- Salpingitis, which is inflammation in the fallopian tubes;
- Infections in the uterus and fallopian tubes, usually caused by sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia and gonorrhea;
- Appendicitis with ruptured appendix, as it can cause infection in the tubes;
- Previous tubal pregnancy;
- Gynecological or abdominal surgeries.
Tuberculosis and abdominal or uterine surgeries can leave scars that obstruct the tubes and prevent the passage of the egg, preventing pregnancy.
Thus, it is common for tubal obstruction to occur due to other gynecological problems such as Endometriosis, so it is important to go to the gynecologist once a year and use condoms to prevent sexually transmitted diseases, which can also cause tubal obstruction.