Treatment for infectious mononucleosis can be done with analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Paracetamol, Ibuprofen or Aspirin to relieve pain and fever, antiviral drugs, such as Aciclovir, for example to decrease virus production, rest, without being able to go to work until the fever disappears and the symptoms pass, and the ingestion of about 2 liters of water a day for the patient to stay hydrated.
Usually, the treatment lasts about 2 to 3 weeks and the general practitioner is best suited to indicate the best treatment.
A great natural treatment for mononucleosis is to gargle with salt and water to lessen the pain and inflammation of the throat. See another home remedy for mononucleosis.
Infectious mononucleosis is a viral disease that is transmitted mainly by contact with the saliva of the infected individual and causes symptoms such as fever, headache, pain and inflammation of the throat, swelling of the throat, especially of the neck, whitish plaques in the throat and in the mouth, intense tiredness and enlargement of the spleen.
Mononucleosis is cured when the treatment is performed correctly, however, it is important for the individual to have tests to confirm that the virus has been totally eliminated, as it may not show symptoms and continue to have the virus in the body, and can transmit it to others.
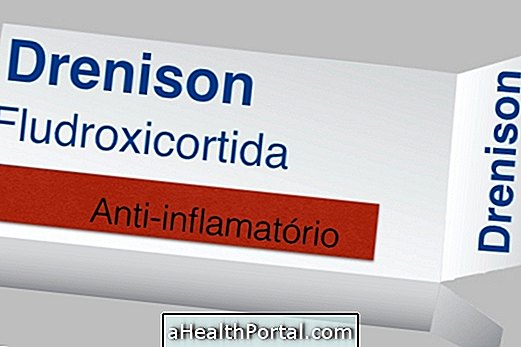
When symptoms are intense and the patient is not responding to medications, treatment can be done with corticosteroids, such as Prednisone, for example. Treatment for mononucleosis with antibiotics is not recommended unless the patient has a bacterial infection secondary to mononucleosis.
Recommendations for mononucleosis
Recommendations for mononucleosis include:
- Wash your hands several times a day, and especially after they have been placed in your mouth;
- Avoid efforts, physical exercises and close contact for about 6 to 8 weeks in order to avoid spleen rupture;
- Avoid kissing;
- Avoid sharing objects contaminated with saliva, such as cutlery, cups or any other utensil that has been placed in the mouth.
These recommendations, with the exception of physical exercise and intimate contact, are also ways of preventing mononucleosis.
Signs of Mononucleosis Improvement
Signs of improvement in mononucleosis include decreased and disappearance of fever, relief of sore throats and headache, decrease and disappearance of swelling of the throat and disappearance of whitish plaques of the mouth and throat.
Although the symptoms usually disappear within 2 to 3 weeks, fatigue may persist for months.
Signs of worsening of mononucleosis
Signs of worsening mononucleosis include severe abdominal pain, enlarged neck, increased inflammation and sore throat, and increased fever.
When the individual shows signs of worsening, it may be necessary to be hospitalized to receive the medicine through the vein.
Complications of mononucleosis
The complications of mononucleosis arise when it is not properly treated and can be meningitis, spleen rupture, throat infection, hepatitis, convulsion and uncoordinated movements, for example.
Treatment for infant mononucleosis
Treatment for infantile mononucleosis is usually done at home, as the child should remain at rest until symptoms improve and should not go to school during this time and also includes analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by the pediatrician, with the exception of aspirin, as it can cause Reye's syndrome, in which inflammation of the brain occurs and accumulation of fat in the liver.
In addition, it is important to provide fluids to the child so they do not dehydrate.
Homeopathic treatment for mononucleosis
Homeopathic treatment for mononucleosis can be done with the Lymphomyosot drops and Mercurius Solubilis tablets which serve to decrease inflammation of the throat, as well as swelling of the throat. These remedies must be indicated by the homeopath and under the guidance of the physician.
Useful links:
- Home Remedy for Mononucleosis
- Treatment for toxoplasmosis
- Symptoms of Mononucleosis