The Schmorl's nodule, also called the Schmorl hernia, consists of a herniated disc that runs into the vertebra. Usually it is found on a MRI or CT scan of the spine, and is not always a cause for concern because it does not cause pain or any other change.
This type of hernia is more common at the end of the thoracic spine and beginning of the lumbar, like between L5 and S1, being more found in people over 45 years of age, but it is not serious, nor is cancer.
Symptoms of Schmorl Nodule
The Schmorl nodule can occur in a healthy spine, with no symptoms present, so when a person does a spinal examination for presenting back pain and finds this nodule, you should continue looking for other changes that are causing the pain in the spine, since this nodule does not cause symptoms, is not serious, nor is it cause for concern.
However, although it is much less common, when the lump forms suddenly, such as during a traffic accident, for example, it can cause a small local inflammation, causing pain in the spine.
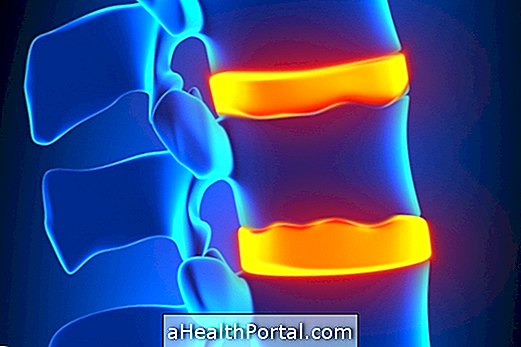
Causes of Schmorl's Nodule
The causes are not fully understood but there are theories that indicate that Schmorl's nodule can be caused by:
- High impact injuries such as in the event of a motorcycle accident or when a person falls by first banging his head on the ground,
- Repetitive trauma, when the person who lifts heavy objects above the head often;
- Degenerative diseases of the vertebral disc ;
- Due to diseases such as osteomalacia, hyperparathyroidism, Paget's disease, infections, cancer or osteoporosis;
- Reaction of the immune system, which begins to act on the disc, when it is inside a vertebra;
- Genetic alteration during the formation of the vertebrae during gestation.
The best exam to see this nodule is the MRI scan that also lets you see if there is swelling around it, which indicates a recent inflamed nodule. When the lump has formed long ago and there is calcification around it, it may be seen on an x-ray, in which case it usually does not cause pain.
Does Schmorl's Node have a cure?
Treatment is only necessary when symptoms are present. In that case one should know what is causing symptoms such as muscle tension, other types of herniated disc, osteoporosis osteomalacia, hyperparathyroidism, Paget's disease, infections and cancer, for example. The treatment can be done with analgesics for pain relief, use of anti-inflammatories and physiotherapy. When there are other important changes in the spine, the orthopedist may indicate the need and have surgery to fuse two vertebrae of the spine, for example.