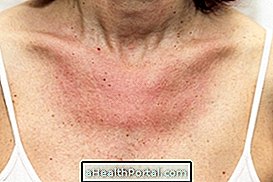
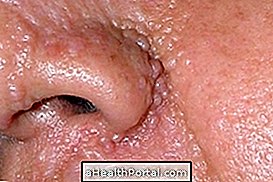
Exfoliative dermatitis, or erythroderma, is an inflammation of the skin that causes scaling and redness in large areas of the body, such as the chest, arms, feet, or legs.
Exfoliative dermatitis is usually caused by other chronic skin problems such as psoriasis or eczema, however, the problem can also be caused by overuse of medicines such as penicillin, phenytoin or barbiturate medications, for example.
Exfoliative dermatitis is curable and its treatment must be done in the hospital, under the guidance of a dermatologist.
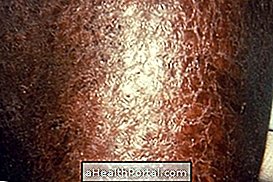

Main symptoms
The main symptoms of exfoliative dermatitis include:
- Redness and irritation of the skin;
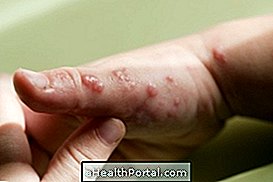
- Formation of skin crusts;
- Loss of hair in affected areas;
- Fever above 38º C and chills;
- Swollen lymph glands;
- Feeling cold due to loss of heat in affected areas.
Exfoliative dermatitis is a serious disease that leaves the body vulnerable to infections, because the skin, which is the tissue that protects the body from aggressive agents, is compromised and, in turn, does not fulfill its duty. Thus, the microorganisms can easily cross it and reach the inner tissues of the body, generating opportunistic infections.
Thus, when there is suspicion of exfoliative dermatitis, it is recommended to go to the emergency room to evaluate the problem and initiate appropriate treatment, avoiding the appearance of complications such as skin infections, generalized infection and even cardiac arrest.
Treatment for Exfoliative Dermatitis
Treatment for exfoliative dermatitis should be started as soon as possible in the hospital, so it is important to go to the ER as soon as the first symptoms appear.
The patient usually needs to be hospitalized for at least 3 days to make liquids and medications directly into the vein, as well as to make oxygen. In addition, your doctor may also indicate:
- Avoid taking very hot baths, giving preference to baths with cold shower;
- Make a protein rich diet, such as chicken, egg or fish, for example, because dermatitis causes loss of protein;
- Apply steroid creams, such as betamethasone or dexamethasone, which should be applied to the skin about 3 times a day to relieve inflammation and itching;
- Apply emollient creams, to moisturize the skin and decrease the peeling of the layers of skin;
- Use antibiotics to fight infections that may be developing in the sites of skin peeling.
In cases where it is possible to identify the specific cause of exfoliative dermatitis, the doctor may also indicate another more appropriate treatment. Thus, if the problem is being caused by the use of a drug, that remedy must be stopped and replaced by another, for example.
Signs of improvement of exfoliative dermatitis
Signs of improvement in exfoliative dermatitis appear about 2 days after initiation of treatment and include relief of itching, decrease in body temperature and reduction of skin peeling.
Signs of worsening of exfoliative dermatitis
Signs of worsening of exfoliative dermatitis arise when treatment is not adequately done at the hospital and include skin wounds, increased body temperature, difficulty moving affected limbs or burning the skin, for example, especially caused by infection of the layers of skin.